
Data Sovereignty for Manufacturing Businesses
Data has become a valuable asset for businesses across all industries. Manufacturing businesses, in particular, rely heavily on data to improve operational efficiency, optimize supply chains, and enhance decision-making processes. However, with the increasing importance of data comes a new challenge – data sovereignty. Understanding the concept of data sovereignty is crucial for manufacturing businesses to navigate the legal complexities and ensure compliance with international data protection regulations.
What Data Compliance Standards Matter?
Understanding the Concept of Data Sovereignty
Data sovereignty refers to the concept that data is subject to the laws and regulations of the country in which it is located. It emphasizes the control and ownership of data, ensuring that organizations have the power to determine how their data is collected, processed, and stored. With data sovereignty, businesses can safeguard sensitive information and maintain their competitive edge in the global market.
As businesses increasingly rely on data to drive decision-making processes, it becomes imperative to have control over where and how that data is stored. This concept recognizes that data is not just a commodity but a valuable asset that requires protection.
Definition and Importance of Data Sovereignty
Data sovereignty can be defined as the legal right of a business to exercise control over its data. It is crucial for manufacturing businesses as it allows them to protect intellectual property, customer information, and trade secrets from unauthorized access or use. By maintaining data sovereignty, businesses can also mitigate the risks associated with data breaches and cyberattacks.
Manufacturing businesses deal with a vast amount of sensitive data, including product designs, manufacturing processes, and supply chain information. This data is often the result of years of research, development, and innovation. Therefore, it is of utmost importance to ensure that this valuable information remains secure and within the control of the business itself.
Data sovereignty also plays a significant role in compliance with various data protection regulations. Different countries have different laws regarding data privacy and security. By adhering to data sovereignty principles, businesses can ensure that they comply with the specific regulations of the countries in which they operate, avoiding potential legal complications and penalties.
The Role of Data Sovereignty in Manufacturing
In the manufacturing industry, data sovereignty plays a pivotal role in safeguarding critical information related to product designs, manufacturing processes, and supply chain management. It ensures that manufacturing businesses have the autonomy to make informed decisions regarding data access, storage, and sharing, without compromising sensitive information to external entities.
Manufacturing businesses often collaborate with various partners, including suppliers, distributors, and contractors. While these collaborations are essential for a smooth supply chain, they also introduce potential risks to data security. Data sovereignty allows manufacturing businesses to establish clear guidelines and protocols for data sharing, ensuring that only authorized individuals or entities have access to sensitive information.
Furthermore, data sovereignty enables manufacturing businesses to maintain a competitive advantage in the global market. By having control over their data, businesses can protect their proprietary knowledge, innovative ideas, and unique manufacturing processes. This protection prevents unauthorized replication or theft of intellectual property, safeguarding the business’s position in the industry.
Overall, data sovereignty is a critical consideration for manufacturing businesses in today’s interconnected world. It provides the necessary framework for protecting sensitive information, complying with data protection regulations, and maintaining a competitive edge. By understanding and implementing data sovereignty principles, manufacturing businesses can ensure the security and integrity of their data assets.
The Legal Landscape of Data Sovereignty
As data is increasingly being recognized as a valuable asset, governments around the world have enacted laws and regulations to protect data privacy and ensure data sovereignty. Manufacturing businesses need to navigate this complex legal landscape to ensure compliance and avoid costly penalties and reputational damage.
Data sovereignty refers to the concept that data is subject to the laws and regulations of the country in which it is stored or processed. This means that manufacturing businesses operating in multiple countries must understand and adhere to the data protection regulations of each jurisdiction.
One of the key international data protection regulations is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) implemented by the European Union (EU). The GDPR establishes strict rules regarding the collection, processing, and transfer of personal data. Manufacturing businesses operating within the EU or handling data of EU citizens must adhere to these regulations to maintain data sovereignty.
The GDPR not only requires businesses to obtain explicit consent from individuals for data processing but also grants individuals the right to access, rectify, and erase their personal data. This places an additional burden on manufacturing businesses to implement robust data management systems and processes to ensure compliance.
Compliance with data sovereignty regulations can be particularly challenging for manufacturing businesses. They often operate on a global scale, with data being generated, shared, and stored across different jurisdictions. This means that businesses must have a comprehensive understanding of the data protection laws in each country and implement appropriate measures to ensure compliance.
In addition to the GDPR, there are other data protection regulations that manufacturing businesses need to consider. For example, in the United States, the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) grants consumers the right to know what personal information is being collected about them and the right to opt-out of the sale of their personal information. Manufacturing businesses operating in California must comply with these regulations to maintain data sovereignty.
Ensuring compliance with multiple international data protection regulations requires comprehensive data management strategies and robust cybersecurity protocols. Manufacturing businesses need to implement measures such as data encryption, access controls, and regular data audits to protect sensitive information and maintain data sovereignty.
Furthermore, manufacturing businesses should also consider the implications of data sovereignty on their supply chain. If they work with third-party vendors or partners who handle their data, they need to ensure that these entities also comply with relevant data protection regulations to avoid any breaches that could impact their own compliance efforts.
In conclusion, the legal landscape of data sovereignty is complex and ever-evolving. Manufacturing businesses must stay informed about the latest regulations and adapt their data management practices accordingly. By prioritizing data protection and compliance, businesses can maintain data sovereignty, protect their reputation, and build trust with their customers.
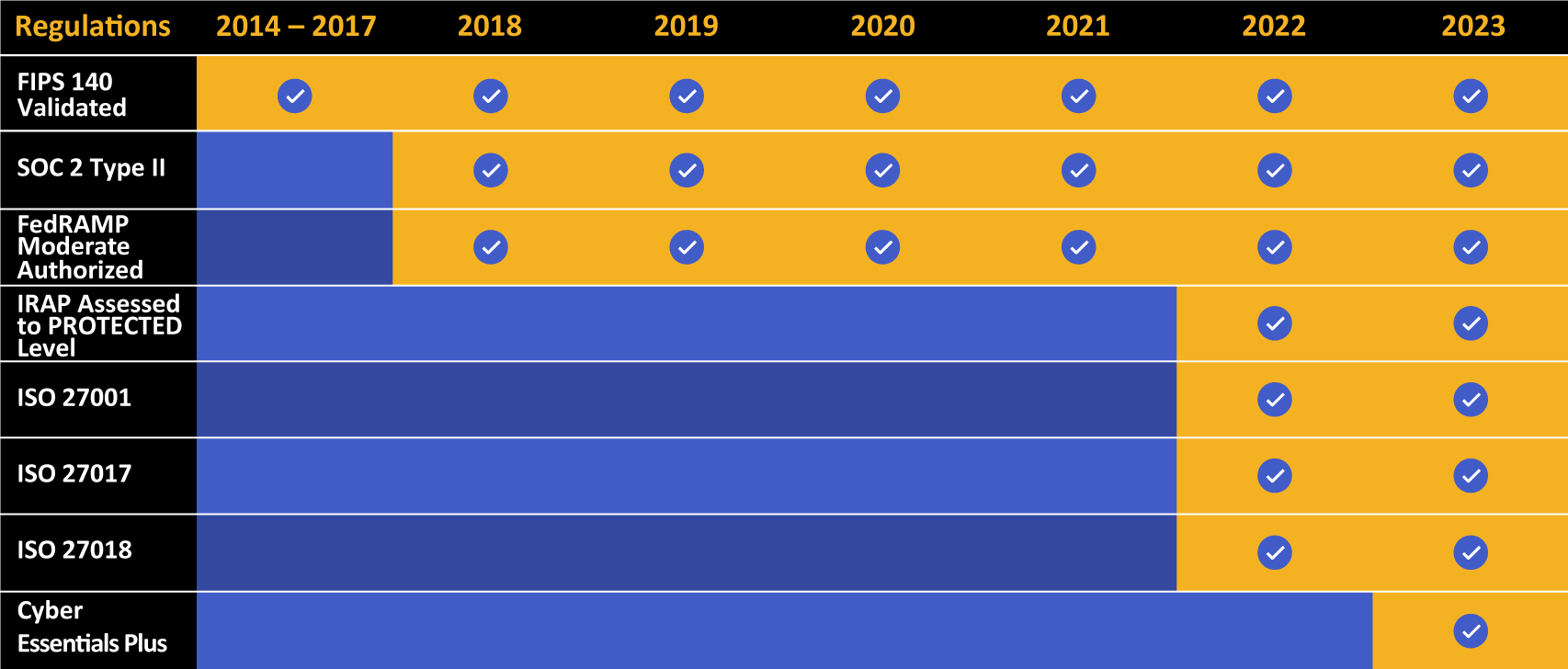
Kiteworks touts a long list of compliance and certification achievements.
Implications of Data Sovereignty for Manufacturing Businesses
Implementing data sovereignty measures can have far-reaching implications for manufacturing businesses, influencing their data management strategies, business partnerships, and supply chain operations.
Data sovereignty refers to the concept that data is subject to the laws and regulations of the country in which it is stored or processed. This means that manufacturing businesses must consider the legal and regulatory requirements of the jurisdictions in which they operate when managing their data.
Impact on Data Management Strategies
Data sovereignty necessitates a shift in data management strategies for manufacturing businesses. They need to identify and classify data based on its sensitivity and ensure that appropriate security measures are in place to protect it.
Manufacturing businesses must carefully assess the sensitivity of their data and determine which data needs to be stored locally or within specific jurisdictions. This may involve conducting risk assessments and implementing data classification frameworks to ensure that data is appropriately protected.
In addition to data classification, manufacturing businesses may need to implement encryption, access controls, and data backup systems to safeguard their data. These measures help to mitigate the risk of data breaches and ensure compliance with data sovereignty regulations.
Influence on Business Partnerships and Supply Chains
Data sovereignty also affects the way manufacturing businesses collaborate with partners and manage their supply chains. They need to establish data sharing agreements and contracts that align with their data sovereignty requirements.
Manufacturing businesses may opt for local data hosting providers and vendors to ensure compliance with specific jurisdictional regulations. This decision can impact their choice of business partners and suppliers, as they must ensure that these entities also adhere to data sovereignty requirements.
Furthermore, manufacturing businesses must consider the potential impact of data sovereignty on their supply chain operations. They may need to implement additional security measures and protocols to protect data as it is shared and transferred between different entities within the supply chain.
Collaboration and communication with partners and suppliers become crucial in ensuring that data sovereignty requirements are met throughout the entire supply chain. This may involve regular audits, assessments, and ongoing monitoring to ensure compliance and mitigate any potential risks.
In conclusion, data sovereignty has significant implications for manufacturing businesses. It requires a shift in data management strategies, including data classification, security measures, and compliance with jurisdictional regulations. It also influences the way businesses collaborate with partners and manage their supply chains, necessitating the establishment of data sharing agreements and the careful selection of vendors and suppliers. By understanding and addressing these implications, manufacturing businesses can navigate the complexities of data sovereignty and ensure the protection and compliance of their data.
Implementing Data Sovereignty in Manufacturing
Implementing data sovereignty in manufacturing requires a systematic approach and a clear understanding of the potential obstacles that may arise. Manufacturing businesses need to proactively address these challenges to achieve data sovereignty effectively.
Steps Towards Achieving Data Sovereignty
Manufacturing businesses can take several steps to achieve data sovereignty. This includes conducting a thorough data audit to identify the types of data they possess and their locations. They should then implement appropriate data protection measures, such as data encryption and access controls.
Overcoming Potential Obstacles
Implementing data sovereignty may face obstacles such as data residency requirements, cross-border data transfers, and conflicting legal frameworks. Manufacturing businesses need to develop strategies to navigate these obstacles, including establishing data governance frameworks, seeking legal counsel, and collaborating with technology partners with expertise in data sovereignty compliance.
Future Trends in Data Sovereignty
Data sovereignty is an evolving field, shaped by changes in laws, regulations, and technological advancements. Keeping an eye on future trends is vital for manufacturing businesses to stay ahead of the curve and ensure ongoing compliance.
Predicted Changes in Data Laws and Regulations
As technology continues to advance, data laws and regulations are expected to become more stringent and comprehensive. Manufacturing businesses should anticipate these changes and invest in robust data management systems and cybersecurity measures to adapt to evolving data sovereignty requirements.
The Future of Manufacturing in a Data Sovereign World
In a data sovereign world, manufacturing businesses that prioritize data sovereignty will gain a competitive advantage. They will have enhanced data protection capabilities, increased customer trust, and improved compliance with international data protection regulations. Embracing data sovereignty will become a critical factor in ensuring long-term success in the manufacturing industry.
Kiteworks Helps Manufacturing Organizations Comply with Data Sovereignty Requirements
Data sovereignty is of paramount importance for manufacturing businesses. It empowers them to protect their valuable data, comply with international data protection regulations, and make informed decisions regarding data management. By understanding the concept of data sovereignty, navigating the legal landscape, and implementing data sovereignty measures, manufacturing businesses can position themselves for success in a data-driven world.
The Kiteworks Private Content Network, a FIPS 140-2 Level 1 validated secure file sharing and file transfer platform, consolidates email, file sharing, web forms, SFTP and managed file transfer, so organizations control, protect, and track every file as it enters and exits the organization.
Kiteworks plays a crucial role in manufacturing organizations’ data sovereignty efforts. For example, Kiteworks’ encryption and access control features protect personal information during cross-border transfers, ensuring secure transmission.
Kiteworks’ extensive deployment options, including private, hybrid, and FedRAMP virtual private cloud, can be configured to store data in specific geographic locations. By storing data in specific locations, organizations can ensure that they are adhering to the data sovereignty laws of the countries in which they operate.
Kiteworks also supports data portability requirements by enabling users to securely access, transfer, and download their personal information. Kiteworks also provides organizations with the ability to establish opt-in mechanisms and procedures for data collection, detailed consent forms, and minor consent procedures. These features help organizations comply with consent requirements, which are a key aspect of data sovereignty.
Finally, Kiteworks’ detailed audit trail enables organizations to prove their compliance with data sovereignty laws to auditors.
Kiteworks deployment options include on-premises, hosted, private, hybrid, and FedRAMP virtual private cloud. With Kiteworks: control access to sensitive content; protect it when it’s shared externally using automated end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and security infrastructure integrations; see, track, and report all file activity, namely who sends what to whom, when, and how.
Finally demonstrate compliance with regulations and standards like GDPR, HIPAA, CMMC, Cyber Essentials Plus, IRAP, and many more.
To learn more about Kiteworks, schedule a custom demo today.
Additional Resources
- Brief Expand Visibility and Automate Protection of All Sensitive Email
- Brief Navigate the Digital Trifecta of Data Sovereignty, Cybersecurity, and Compliance With Kiteworks
- Blog Post Data Sovereignty and GDPR [Understanding Data Security]
- Blog Post What Is Email Security? How to Protect Your Sensitive Content With Email Security
- Brief Secure Protocol Package: Strengthening Data Exchange With SFTP and SMTP