
Data Sovereignty for Government Agencies
Data sovereignty is a concept that has gained significant importance in recent years, especially for government agencies. It refers to the idea that data collected and generated by individuals or organizations should be stored and processed within the geographical boundaries of the country where it was collected. This ensures that governments have control over their citizens’ data and protects it from unauthorized access or misuse by foreign entities.
What Data Compliance Standards Matter?
Understanding the Concept of Data Sovereignty
Before delving into the details of data sovereignty for government agencies, it is essential to understand what data sovereignty means and why it’s important.
Data sovereignty can be defined as the legal and political concept that dictates data created and collected within a country’s borders should remain under the jurisdiction of that country.
The importance of data sovereignty for government agencies cannot be overstated. It ensures that governments can exercise control over sensitive information critical to national security, public welfare, and economic development. By having sovereignty over their data, government agencies can foster trust among citizens and safeguard national interests.
Data sovereignty goes beyond mere control and ownership of data. It also encompasses the responsibility of governments to protect and manage data in a manner that aligns with their national interests and values. This includes implementing robust data protection measures, ensuring data privacy, and complying with relevant laws and regulations.
Moreover, data sovereignty plays a crucial role in the operations of government agencies. It provides them with the authority to define how data is collected, stored, and shared. This allows governments to implement appropriate security measures, data protection policies, and ensure compliance with relevant laws and regulations. Furthermore, data sovereignty empowers governments to make informed decisions based on accurate and complete information, enabling effective governance.
Government agencies rely on data to fulfill their various functions and responsibilities. Whether it is managing public services, formulating policies, or conducting research, data sovereignty ensures that governments have access to reliable and up-to-date information. This, in turn, enables them to make evidence-based decisions and effectively address the needs and concerns of their citizens.
Furthermore, data sovereignty is closely linked to national sovereignty. It is an essential component of a country’s digital independence and resilience. By asserting control over their data, governments can reduce their dependence on foreign entities and mitigate the risks associated with data breaches, cyberattacks, and unauthorized access. This enhances a country’s ability to protect its critical infrastructure, maintain national security, and safeguard its economic interests.
Data sovereignty is a vital concept for government agencies. It empowers governments to exercise control over their data, protect national interests, and make informed decisions. By understanding and embracing data sovereignty, government agencies can ensure the effective and secure management of data, fostering trust among citizens and promoting national development.
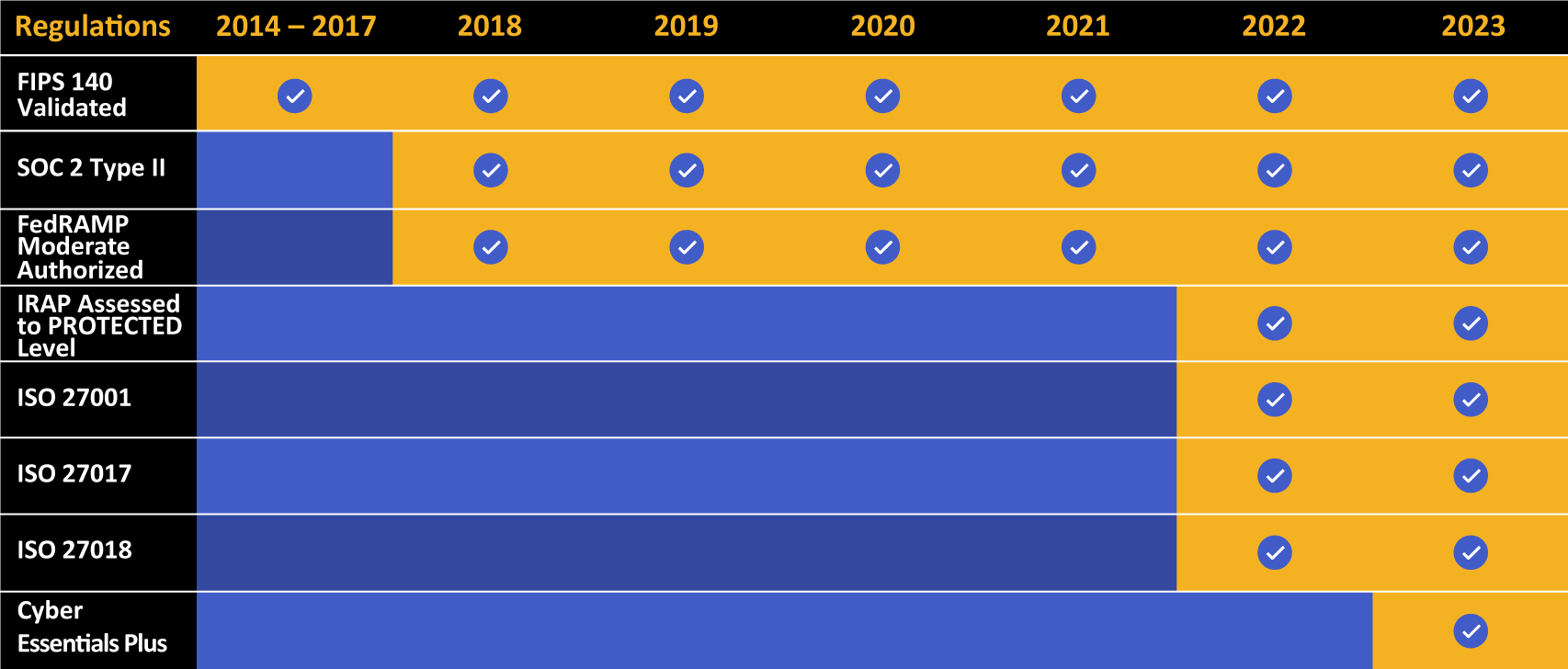
Kiteworks touts a long list of compliance and certification achievements.
The Legal Framework Surrounding Data Sovereignty
While data sovereignty is an essential concept, its implementation requires a robust legal framework to ensure compliance and protect data privacy. However, understanding the legal landscape surrounding data sovereignty involves delving into various international and national laws and regulations.
International Laws and Regulations
At the international level, several laws and regulations govern data sovereignty. These regulations aim to establish the rights of individuals regarding their personal data and impose restrictions on data transfer outside their respective jurisdictions.
One of the most prominent international regulations is the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union. The GDPR sets out strict guidelines for how organizations should handle personal data, ensuring that individuals have control over their information and that it is adequately protected. It requires organizations to obtain explicit consent from individuals before collecting and processing their data, and it grants individuals the right to access, rectify, and erase their personal information.
In addition to the GDPR, many countries have their own data protection laws that align with international standards. For instance, Australia has the Privacy Act 1988, which regulates the handling of personal information by Australian government agencies and businesses. Similarly, Canada has the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA), which governs how private-sector organizations collect, use, and disclose personal information.
National Laws and Policies
Each country has its laws and policies that govern data sovereignty, reflecting their unique cultural, political, and legal contexts. These regulations define how data should be handled, stored, and shared within national borders.
For example, in the United States, the Federal Data Protection Act outlines the framework for data handling by government agencies and imposes stringent penalties for non-compliance. This act ensures that government agencies handle data responsibly and prioritize the protection of citizens’ personal information.
Similarly, in India, the Personal Data Protection Act aims to regulate the processing of personal data by individuals, companies, and the government. It establishes principles for data protection, consent requirements, and the establishment of a Data Protection Authority to oversee compliance.
Furthermore, some countries have specific policies that address data sovereignty in the context of national security. These policies aim to protect sensitive data from being accessed or stored in foreign jurisdictions. For instance, China has implemented the Cybersecurity Law, which requires critical information infrastructure operators to store personal information and important data within China’s borders.
Overall, the legal framework surrounding data sovereignty is a complex web of international and national laws and regulations. These laws aim to strike a balance between protecting individuals’ privacy rights and facilitating the free flow of data necessary for innovation and economic growth.
Challenges in Implementing Data Sovereignty
Implementing data sovereignty for government agencies comes with its set of challenges that need to be addressed effectively to ensure its successful adoption.
Data sovereignty refers to the concept of a country or government having full control and ownership over the data generated within its borders. It is an important aspect of national security and privacy, as it ensures that sensitive data is protected and governed by the laws and regulations of the country.
However, the implementation of data sovereignty is not without its challenges. Let’s explore some of the key challenges that governments face in this process:
Technological Challenges
One of the primary challenges is the technological infrastructure required to store and process vast amounts of data within national boundaries. Upgrading legacy systems and establishing secure data centers can be a costly and complex endeavor.
Modernizing the technological infrastructure involves investing in robust hardware and software solutions that can handle the increasing volume and complexity of data. This includes high-performance servers, storage systems, and networking equipment.
Furthermore, ensuring the security of the data is of utmost importance. Government agencies need to invest in advanced security measures to protect data from cyber threats, as data sovereignty necessitates heightened security measures. This includes implementing firewalls, encryption protocols, and intrusion detection systems.
Moreover, governments also need to consider the scalability and flexibility of their infrastructure. As data continues to grow exponentially, the infrastructure should be able to accommodate future expansion and evolving technologies.
Policy and Regulatory Challenges
Data sovereignty often requires governments to establish new policies and laws that align with the concept. This may involve updating existing data protection laws, establishing data localization requirements, and defining penalties for non-compliance.
Creating a comprehensive legal framework that supports data sovereignty can be a complex task. Governments need to consult with legal experts, industry stakeholders, and privacy advocates to ensure that the policies and regulations strike the right balance between protecting data and fostering innovation.
However, striking a balance between data sovereignty and promoting data-driven innovation can be a challenge. Governments need to find a middle ground that allows them to control data while still enabling data-driven research and development. This requires careful consideration of factors such as data sharing agreements, cross-border data transfers, and collaboration with international partners.
Additionally, governments must also address the issue of data sovereignty in the context of cloud computing. As more government agencies adopt cloud services, ensuring that the data remains within national boundaries becomes a challenge. Governments need to negotiate with cloud service providers to establish data sovereignty agreements and ensure that the data is stored and processed in compliance with the country’s regulations.
In conclusion, implementing data sovereignty is a complex undertaking that requires governments to address technological, policy, and regulatory challenges. By investing in robust infrastructure, updating laws and regulations, and fostering collaboration, governments can successfully navigate these challenges and ensure the protection and control of their data.
Strategies for Achieving Data Sovereignty
To overcome the challenges associated with implementing data sovereignty, government agencies can adopt specific strategies and best practices.
Data sovereignty is a crucial concept for government agencies as it ensures that sensitive data remains within their control and jurisdiction. It allows governments to protect the privacy and security of their citizens’ data, prevent unauthorized access, and maintain regulatory compliance.
Building a Robust Data Infrastructure
Government agencies need to invest in building a robust data infrastructure that supports data sovereignty. This includes upgrading network capabilities, adopting cloud technologies, and establishing secure data centers within the country.
By having a modern and reliable infrastructure, government agencies can ensure that data remains within their control. Upgrading network capabilities allows for faster and more secure data transfer, reducing the risk of data breaches or unauthorized access. Adopting cloud technologies provides scalable and flexible storage solutions, enabling efficient data management while maintaining sovereignty. Establishing secure data centers within the country ensures that sensitive data is stored within the jurisdiction, minimizing the risk of data being subject to foreign laws or regulations.
Formulating Effective Data Policies
An essential aspect of achieving data sovereignty is formulating effective data policies that outline how data should be handled, collected, and shared.
These policies should be aligned with existing laws and regulations and take into account the specific needs and requirements of government agencies. They should address issues such as data classification, access control, data retention, and data sharing agreements.
By formulating comprehensive and clear data policies, government agencies can ensure that data sovereignty is achieved while remaining in compliance with legal and regulatory frameworks. These policies should also include mechanisms for regular audits and assessments to ensure ongoing adherence to data sovereignty principles.
Furthermore, government agencies should consider engaging with stakeholders, including industry experts, privacy advocates, and the public, to gather input and feedback on data policies. This collaborative approach can help build trust and ensure that data sovereignty measures are implemented in a transparent and accountable manner.
In conclusion, achieving data sovereignty requires a multi-faceted approach that includes building a robust data infrastructure and formulating effective data policies. By investing in these strategies, government agencies can protect sensitive data, maintain control over its storage and management, and ensure compliance with legal and regulatory requirements.
The Future of Data Sovereignty in Government Agencies
The concept of data sovereignty for government agencies is likely to evolve in the coming years, driven by emerging trends and innovations.
Emerging Trends and Innovations
Advancements in technologies such as blockchain, artificial intelligence, and edge computing are likely to play a significant role in shaping the future of data sovereignty. These technologies offer new possibilities for secure data storage, processing, and sharing within national borders.
Moreover, international collaborations and discussions among governments are expected to influence data sovereignty frameworks, facilitating greater compatibility and cooperation between countries.
Long-term Implications and Opportunities
Data sovereignty presents governments with numerous opportunities to enhance cybersecurity, protect national interests, and ensure data privacy for their citizens. It also allows for the development of domestic data-driven industries, fostering economic growth and innovation.
However, maintaining data sovereignty may require governments to balance national interests with international collaboration and interoperability, ensuring harmonization across borders while protecting their sovereignty.
Kiteworks Helps Government Agencies Comply with Data Sovereignty Requirements
Data sovereignty is a critical concept for government agencies, ensuring control and governance over data collected within their jurisdiction. By understanding data sovereignty, adopting robust legal frameworks, and implementing effective strategies, government agencies can navigate the challenges and harness the benefits of data sovereignty for the betterment of their nations.
The Kiteworks Private Content Network, a FIPS 140-2 Level 1 validated secure file sharing and file transfer platform, consolidates email, file sharing, web forms, SFTP and managed file transfer, so organizations control, protect, and track every file as it enters and exits the organization.
Kiteworks plays a crucial role in government agencies’ data sovereignty efforts. For example, Kiteworks’ encryption and access control features protect personal information during cross-border transfers, ensuring secure transmission.
Kiteworks’ extensive deployment options, including private, hybrid, and FedRAMP virtual private cloud, can be configured to store data in specific geographic locations. By storing data in specific locations, organizations can ensure that they are adhering to the data sovereignty laws of the countries in which they operate.
Kiteworks also supports data portability requirements by enabling users to securely access, transfer, and download their personal information. Kiteworks also provides organizations with the ability to establish opt-in mechanisms and procedures for data collection, detailed consent forms, and minor consent procedures. These features help organizations comply with consent requirements, which are a key aspect of data sovereignty.
Finally, Kiteworks’ detailed audit trail enables organizations to prove their compliance with data sovereignty laws to auditors.
With Kiteworks: control access to sensitive content; protect it when it’s shared externally using automated end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and security infrastructure integrations; see, track, and report all file activity, namely who sends what to whom, when, and how.
Finally demonstrate compliance with regulations and standards like GDPR, HIPAA, CMMC, Cyber Essentials Plus, IRAP, and many more.
To learn more about Kiteworks, schedule a custom demo today.
Additional Resources
- Brief Expand Visibility and Automate Protection of All Sensitive Email
- Brief Navigate the Digital Trifecta of Data Sovereignty, Cybersecurity, and Compliance With Kiteworks
- Blog Post Data Sovereignty and GDPR [Understanding Data Security]
- Video What Is Email Security? How to Protect Your Sensitive Content With Email Security
- Brief Secure Protocol Package: Strengthening Data Exchange With SFTP and SMTP