
Data Sovereignty Dos and Don’ts
Data sovereignty is a critical concept in today’s digital world. As businesses and individuals increasingly rely on data to drive decision-making, protect sensitive information, and ensure regulatory compliance, understanding the dos and don’ts of data sovereignty is essential. In this article, we will explore the definition and importance of data sovereignty, delve into the dos and don’ts, discuss the challenges, and look ahead at future trends in this rapidly evolving landscape.
What Data Compliance Standards Matter?
Data Sovereignty Principles
Data sovereignty refers to the legal and technical concept that dictates where data is stored, accessed, and processed. It involves ensuring that data is subject to the laws and regulations of the country or region in which it resides. This means that the data owner retains control over their data and determines how it is used, shared, and protected.
When it comes to data sovereignty, there are several key factors to consider. One of the most important aspects is the protection of national security. By having data stored within the country’s borders, governments can ensure that sensitive information related to national security is not exposed to potential threats from foreign entities. This is especially crucial when it comes to critical infrastructure, such as power grids, transportation systems, and communication networks.
In addition to national security, data sovereignty also plays a vital role in safeguarding personal data and preserving privacy. With the increasing amount of data being collected and processed by organizations, it is essential to have strict regulations in place to protect individuals’ personal information. Data breaches and cyberattacks have become all too common in today’s digital landscape, and data sovereignty helps mitigate these risks by allowing countries to enforce laws that govern access to and use of data.
Definition and Importance of Data Sovereignty
Data sovereignty is crucial for protecting national security, safeguarding personal data, and preserving privacy. It ensures that countries can enforce laws that govern access to and use of data, particularly when it pertains to sensitive information or critical infrastructure. By having control over their data, countries can mitigate the risks associated with data breaches, cyberattacks, and unauthorized access.
Furthermore, data sovereignty also plays a significant role in promoting economic growth and innovation. When businesses have confidence that their data is protected and subject to the laws of the country in which it resides, they are more likely to invest in that country’s economy. This, in turn, leads to job creation, technological advancements, and overall economic prosperity.
The Role of Data Sovereignty in Today’s Business Climate
In today’s digital world, where data flows across borders and regulatory frameworks vary, data sovereignty acts as a safeguard against potential abuses of personal information or intellectual property. It allows organizations to maintain control over their data, prevent unauthorized access, and ensure compliance with data protection regulations. Embracing data sovereignty can also foster trust between businesses and their customers, as it demonstrates a commitment to protecting sensitive data.
Moreover, data sovereignty has become increasingly important due to the rise of cloud computing and the reliance on third-party service providers. With data being stored and processed in remote data centers, it is essential to have clear guidelines and regulations in place to ensure that data remains secure and subject to the laws of the country in which it originates.
It is worth noting that data sovereignty is not without its challenges. In a globalized world where data is constantly being transferred and shared, striking the right balance between data protection and facilitating cross-border data flows can be complex. International agreements and collaborations are necessary to address these challenges and establish a framework that respects data sovereignty while enabling the benefits of a connected world.
The “Do’s” of Data Sovereignty
One of the key dos of data sovereignty is implementing effective data management strategies. This entails understanding what data is collected, where it is stored, how it is processed, and who has access to it. By implementing robust data management practices, organizations can ensure data integrity, minimize the risk of data breaches, and facilitate compliance with data protection regulations.
Data management strategies involve various aspects, such as data classification, data lifecycle management, and data governance. Organizations need to classify their data based on its sensitivity and criticality. This classification helps in determining the appropriate security measures and access controls for different types of data.
Furthermore, organizations need to establish clear data lifecycle management processes. This includes defining how data is collected, stored, processed, and eventually disposed of. By having a well-defined data lifecycle, organizations can ensure that data is only retained for as long as necessary and is securely disposed of when no longer needed.
Data governance is another crucial aspect of effective data management. It involves establishing policies and procedures for data handling, ensuring compliance with regulations, and assigning responsibilities for data management tasks. By implementing strong data governance practices, organizations can maintain data quality, consistency, and accuracy.
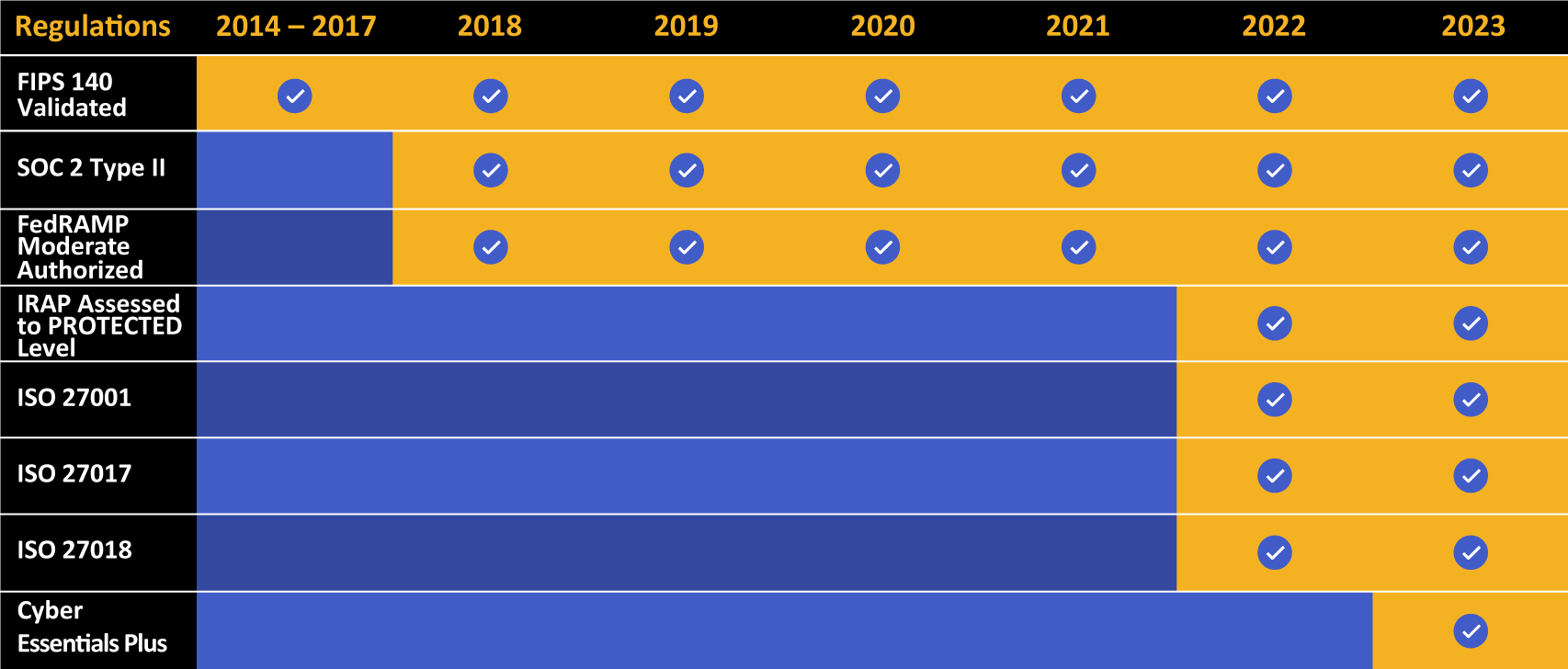
Kiteworks touts a long list of compliance and certification achievements.
Ensuring Compliance with Global Data Protection Regulations
Compliance with global data protection regulations is another crucial aspect of data sovereignty. Organizations must stay up to date with the ever-evolving landscape of data protection laws and ensure that they adhere to the regulations applicable in the jurisdictions in which they operate. This may involve obtaining proper consent, implementing robust security measures, and regularly auditing data handling practices.
Global data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, require organizations to obtain explicit consent from individuals before collecting and processing their personally identifiable and protected health information (PII/PHI). This means that organizations need to have mechanisms in place to obtain consent and provide individuals with clear information about how their data will be used.
In addition to obtaining consent, organizations need to implement robust security measures to protect personal data from unauthorized access, disclosure, and alteration. This includes measures such as encryption, access controls, and regular security audits. By implementing these security measures, organizations can minimize the risk of data breaches and ensure the confidentiality and integrity of personal data.
Regular auditing of data handling practices is also essential to ensure ongoing compliance with data protection regulations. Organizations should conduct internal audits to assess their data handling processes, identify any gaps or vulnerabilities, and take corrective actions as needed. External audits by independent third parties can also provide an objective assessment of an organization’s compliance with data protection regulations.
Prioritizing Data Security and Privacy
Data security and privacy should be at the forefront of any data sovereignty strategy. This means adopting encryption technologies, implementing access controls, regularly monitoring for suspicious activities, and educating employees about data handling best practices. Organizations should also establish clear policies and procedures for handling personal data and regularly review and update them as needed.
Encryption technologies play a crucial role in protecting data from unauthorized access. Organizations should implement strong encryption algorithms to encrypt data both at rest and in transit. This ensures that even if data is intercepted or stolen, it remains unreadable and unusable without the encryption keys.
Access controls are another important aspect of data security. Organizations should implement role-based access controls to ensure that only authorized individuals have access to sensitive data. This includes implementing strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, and regularly reviewing and updating access privileges based on changes in job roles or responsibilities.
Regular monitoring for suspicious activities is essential to detect and respond to potential security incidents. Organizations should implement security monitoring tools and processes to identify any unusual or unauthorized activities, such as unauthorized access attempts or data exfiltration. By detecting and responding to these incidents in a timely manner, organizations can minimize the impact of security breaches.
Lastly, educating employees about data handling best practices is crucial for maintaining data security and privacy. Organizations should provide regular training and awareness programs to ensure that employees understand their responsibilities and the potential risks associated with mishandling data. This includes training on topics such as phishing awareness, password security, and secure data disposal.
The “Don’ts” of Data Sovereignty
Avoiding common mistakes is essential for maintaining data sovereignty. These mistakes include failing to understand where data is stored and who has access to it, neglecting to implement appropriate security measures, and underestimating the importance of data sovereignty compliance. Organizations must be aware of these pitfalls and take proactive steps to mitigate them.
Risks of Non-Compliance to Data Sovereignty Laws
Non-compliance with data sovereignty laws can have severe consequences. Organizations that fail to comply may face legal penalties, damage to their reputation, loss of customer trust, and potential disruptions to their business operations. It is crucial to recognize the risks associated with non-compliance and take the necessary measures to adhere to data sovereignty regulations.
Avoiding Data Breaches and Loss of Trust
Data breaches can lead to significant financial and reputational damage. Organizations should avoid data breaches by implementing robust security measures, conducting regular risk assessments, and staying vigilant against emerging threats. Building trust with customers and stakeholders is pivotal, and maintaining data sovereignty plays a crucial role in achieving this trust.
Navigating Data Sovereignty Challenges
Navigating the legal and technical challenges of data sovereignty can be complex. Organizations must familiarize themselves with the laws and regulations that govern data sovereignty in each jurisdiction they operate in. They should also ensure that their technical infrastructure and data management processes align with these requirements. Collaborating with legal experts and technology partners can help navigate these challenges effectively.
Adapting to Changing Data Sovereignty Laws
Data sovereignty laws are constantly evolving, and organizations must remain flexible and adaptive. They should closely monitor regulatory changes, conduct regular compliance audits, and update their processes and policies accordingly. By staying proactive, organizations can avoid penalties, maintain data sovereignty, and continue to build trust with their customers.
Future Trends in Data Sovereignty
Emerging technologies, such as cloud computing and artificial intelligence, are shaping the future of data sovereignty. As these technologies continue to evolve, organizations must navigate the implications and challenges they present. They must ensure that their data management strategies align with the capabilities and limitations of these technologies while maintaining compliance with data sovereignty laws.
Predicting the Evolution of Data Sovereignty Laws
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, data sovereignty laws will likely undergo significant changes. Organizations should stay informed about these developments and anticipate how they may impact their operations. By being proactive and adaptable, organizations can position themselves to successfully navigate the evolving regulatory landscape.
Kiteworks Helps Organizations Protect Sensitive Customer Information with Data Sovereignty
Understanding the dos and don’ts of data sovereignty is crucial for organizations seeking to protect their data, ensure compliance with laws and regulations, and maintain customer trust. By implementing effective data management strategies, prioritizing security and privacy, and staying proactive in adapting to emerging trends and regulatory changes, organizations can successfully navigate the challenges of data sovereignty and position themselves for a secure and compliant future.
The Kiteworks Private Content Network, a FIPS 140-2 Level 1 validated secure file sharing and file transfer platform, consolidates email, file sharing, web forms, SFTP and managed file transfer, so organizations control, protect, and track every file as it enters and exits the organization.
Kiteworks plays a crucial role in businesses’ data sovereignty efforts. For example, Kiteworks’ encryption and access control features protect personal information during cross-border transfers, ensuring secure transmission.
Kiteworks’ extensive deployment options, including private, hybrid, and FedRAMP virtual private cloud, can be configured to store data in specific geographic locations. By storing data in specific locations, organizations can ensure that they are adhering to the data sovereignty laws of the countries in which they operate.
Kiteworks also supports data portability requirements by enabling users to securely access, transfer, and download their personal information. Kiteworks also provides organizations with the ability to establish opt-in mechanisms and procedures for data collection, detailed consent forms, and minor consent procedures. These features help organizations comply with consent requirements, which are a key aspect of data sovereignty.
Finally, Kiteworks’ detailed audit trail enables organizations to prove their compliance with data sovereignty laws to auditors.
With Kiteworks: control access to sensitive content; protect it when it’s shared externally using automated end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and security infrastructure integrations; see, track, and report all file activity, namely who sends what to whom, when, and how.
Finally demonstrate compliance with regulations and standards like GDPR, HIPAA, CMMC, Cyber Essentials Plus, IRAP, and many more.
To learn more about Kiteworks, schedule a custom demo today.
Additional Resources
- Brief Expand Visibility and Automate Protection of All Sensitive Email
- Brief Navigate the Digital Trifecta of Data Sovereignty, Cybersecurity, and Compliance With Kiteworks
- Blog Post Data Sovereignty and GDPR [Understanding Data Security]
- Video What Is Email Security? How to Protect Your Sensitive Content With Email Security
- Brief Secure Protocol Package: Strengthening Data Exchange With SFTP and SMTP