
Data Sovereignty Best Practices
Data sovereignty is a critical element in today’s digital landscape. As organizations handle increasing amounts of data, it becomes imperative to understand the best practices for ensuring data sovereignty.
In this post, we will explore the various aspects of data sovereignty, including its definition, importance, legal landscape, key principles, implementation strategies, and challenges.
What Data Compliance Standards Matter?
Understanding Data Sovereignty
Data sovereignty refers to the concept that data is subject to the laws and regulations of the country where it is located. It emphasizes the control and ownership of data by the country or organization that generates it. The importance of data sovereignty has grown exponentially with the rise of the digital economy.
Data sovereignty is not a new concept. It has its roots in the early days of computing when data was primarily stored on physical media such as tapes and disks. However, with the advent of the internet and cloud computing, data can now be stored and processed in multiple locations around the world. This has raised concerns about the control and security of data, leading to the need for data sovereignty laws and regulations.
Definition and Importance of Data Sovereignty
Data sovereignty is the legal concept that dictates who has ownership and control over data. It ensures that data generated within a specific country remains subject to its laws and regulations. The importance of data sovereignty lies in protecting sensitive information, preserving national security, and fostering trust between organizations and their users.
One of the key reasons why data sovereignty is important is the protection of sensitive information. In today’s digital world, data is a valuable asset that can include personal, financial, and proprietary information. By asserting control over their data, countries can enact laws and regulations to safeguard this sensitive information from unauthorized access and misuse.
National security is another critical aspect of data sovereignty. Governments need to have control over data that is vital to their national security interests. This can include data related to defense, intelligence, and critical infrastructure. By having data sovereignty laws in place, countries can ensure that this sensitive information remains within their borders and is protected from foreign interference.
Fostering trust between organizations and their users is also a significant benefit of data sovereignty. When users know that their data is subject to the laws and regulations of their own country, they are more likely to feel confident in sharing their information. This trust is essential for the growth of the digital economy, as it encourages individuals and businesses to embrace new technologies and engage in online transactions.
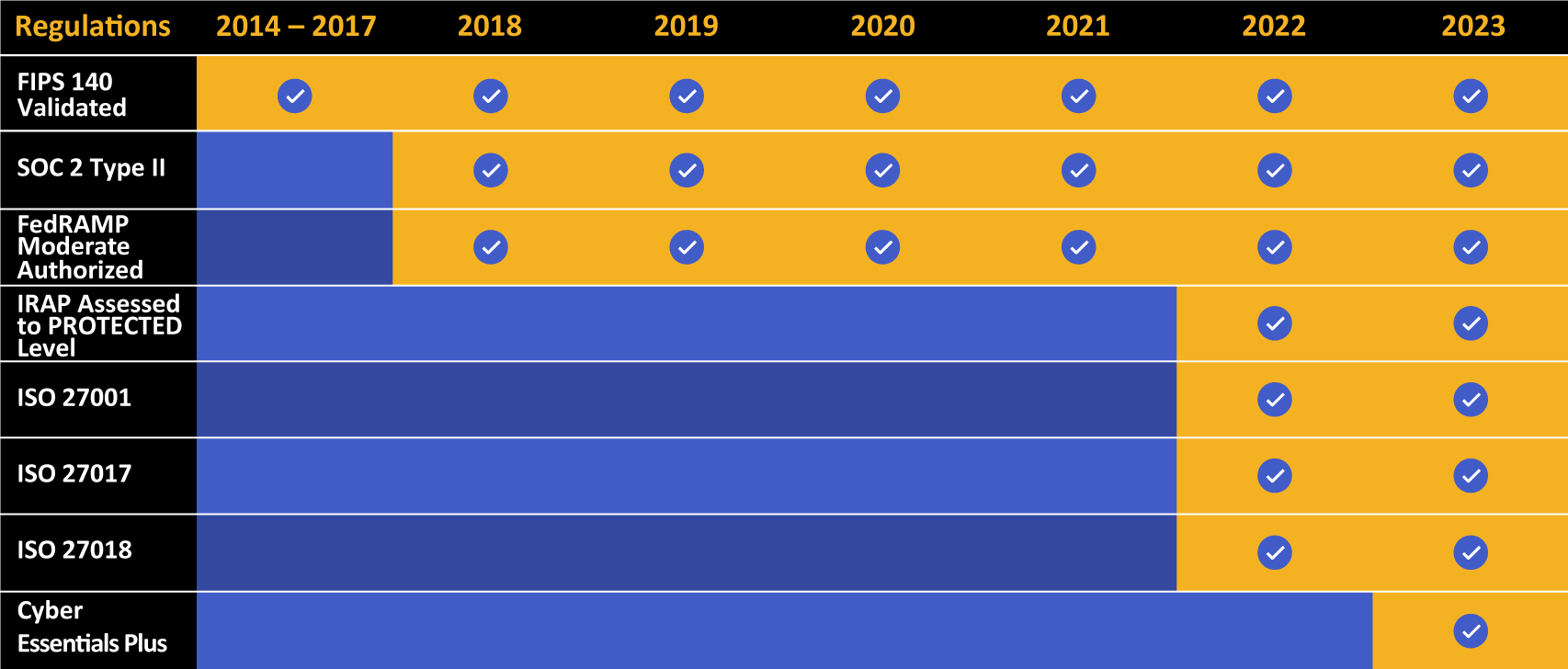
Kiteworks touts a long list of compliance and certification achievements.
The Role of Data Sovereignty in the Modern Business Landscape
In the modern business landscape, data is the new currency. By asserting control over their data, countries can safeguard their economic interests and ensure that the benefits of data-driven innovation stay within their borders. It also enables the development of robust data protection regulations to enhance consumer privacy and security.
Data is a valuable resource that drives innovation, enables personalized services, and fuels economic growth. By having data sovereignty laws in place, countries can ensure that they have the ability to regulate and benefit from the use of data within their jurisdiction. This can include imposing taxes or fees on data transfers, promoting local data storage, or requiring data localization for certain industries.
Data sovereignty also enables countries to develop robust data protection regulations to enhance consumer privacy and security. With the increasing amount of personal data being collected and processed, it is essential to have laws and regulations in place to protect individuals’ rights. Data sovereignty allows countries to establish frameworks for data protection, including consent requirements, data breach notification, and the right to be forgotten.
Furthermore, data sovereignty can foster innovation and economic growth within a country. By having control over their data, countries can encourage the development of local data-driven industries and attract foreign investment. This can lead to job creation, increased competitiveness, and the establishment of data-driven ecosystems that drive economic prosperity.
In conclusion, data sovereignty is a crucial concept in the digital age. It ensures that countries have control and ownership over their data, protecting sensitive information, preserving national security, and fostering trust. By asserting data sovereignty, countries can safeguard their economic interests, enhance consumer privacy and security, and drive innovation and economic growth in the digital economy.
The Legal Landscape of Data Sovereignty
The legal landscape surrounding data sovereignty is complex and constantly evolving. It encompasses global data protection regulations and compliance challenges faced by organizations operating in multiple jurisdictions.
Data sovereignty refers to the concept that data is subject to the laws and regulations of the country in which it is located. This means that organizations must ensure that they comply with the specific data protection regulations of each jurisdiction in which they operate.
Global Data Protection Regulations
Various global data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), set stringent guidelines for data protection, including data sovereignty requirements.
The GDPR, which came into effect in May 2018, is one of the most comprehensive data protection regulations in the world. It applies to all organizations that process the personal data of EU citizens, regardless of where the organization is based. The GDPR requires organizations to implement measures to protect personal data and imposes strict penalties for non-compliance.
The CCPA, which became effective on January 1, 2020, is a state-level data protection regulation in the United States. It grants California residents certain rights over their personal information and requires businesses to be transparent about their data collection and sharing practices.
Organizations must navigate these regulations to ensure compliance and maintain consumer trust. They need to implement robust data protection measures, such as encryption and access controls, and establish clear policies and procedures for handling personal data.
Compliance Challenges in Data Sovereignty
Complying with data sovereignty regulations presents a set of challenges for organizations. These challenges include understanding and managing cross-border data transfer restrictions, addressing conflicting legal requirements across jurisdictions, and maintaining data integrity while adhering to local laws.
Many countries have restrictions on the transfer of personal data outside their borders. These restrictions aim to protect the privacy and security of their citizens’ data. Organizations must ensure that they have appropriate mechanisms in place, such as data transfer agreements or binding corporate rules, to legally transfer data across borders.
Conflicting legal requirements across jurisdictions can also pose challenges. For example, one country may require organizations to retain certain types of data for a specific period, while another country may have data retention laws that contradict those requirements. Organizations need to carefully navigate these conflicting requirements to avoid legal and compliance risks.
Maintaining data integrity while adhering to local laws is another challenge in data sovereignty. Organizations must ensure that they can access and manage their data in compliance with local regulations, while also protecting the privacy and security of that data. This may involve implementing data localization measures, such as storing data within the jurisdiction it originates from.
In conclusion, the legal landscape of data sovereignty is complex and ever-changing. Organizations must stay informed about global data protection regulations, such as the GDPR and CCPA, and navigate the compliance challenges they present. By doing so, organizations can ensure the protection of personal data and maintain consumer trust in an increasingly data-driven world.
Key Principles of Data Sovereignty
To establish effective data sovereignty, organizations need to adhere to key principles that govern data localization and residency, as well as data access and control.
Data sovereignty is a critical concept in today’s digital world, where the volume and value of data continue to grow exponentially. It refers to the idea that nations and organizations should have the ultimate authority and control over the data generated within their borders. This control is vital for various reasons, including national security, privacy protection, and economic development.
Data Localization and Residency
Data localization, one of the key principles of data sovereignty, refers to the requirement that data generated within a country should remain physically stored within its borders. This principle aims to prevent unauthorized access by foreign entities and preserve national security. By keeping data within the country’s jurisdiction, governments can ensure that sensitive information is not exposed to potential risks associated with cross-border data transfers.
However, implementing data localization measures is not without its challenges. Organizations must navigate a complex landscape of laws and regulations that vary from country to country. They need to understand local requirements and implement mechanisms to comply with data residency requirements without compromising operational efficiency. This may involve establishing data centers or partnering with local cloud service providers to store and process data within the country’s borders.
Data Access and Control
Data sovereignty also encompasses the ability to control and govern access to data. Organizations must have robust access control mechanisms, data encryption, and secure authentication protocols to protect sensitive information. By implementing these measures, they can ensure that only authorized individuals or entities can access and manipulate the data.
Moreover, data access and control are crucial for compliance with data privacy regulations. With the increasing number of data breaches and privacy concerns, governments around the world are enacting stringent laws to protect individuals’ personally identifiable and protected health information (PII/PHI). Organizations that fail to comply with these regulations may face severe penalties and damage to their reputation.
Therefore, organizations must invest in technologies and practices that allow them to maintain control over their data. This includes implementing data classification systems, data loss prevention measures, and regular audits to ensure compliance. By maintaining control over data, organizations can prevent unauthorized use and ensure that data is handled in accordance with applicable laws and regulations.
In conclusion, data sovereignty is a complex and multifaceted concept that requires organizations to adhere to key principles such as data localization and residency, as well as data access and control. By understanding and implementing these principles, organizations can navigate the challenges of the digital age while safeguarding their data and complying with relevant regulations.
Implementing Data Sovereignty in Your Organization
Implementing data sovereignty requires a well-defined strategy and the adoption of appropriate technology solutions.
Developing a Data Sovereignty Strategy
An effective data sovereignty strategy involves understanding legal requirements, assessing data risks, establishing policies for data classification and handling, and ensuring regular audits and compliance reviews. Organizations should collaborate with legal experts, data protection officers, and IT teams to develop a comprehensive strategy that aligns with their business objectives.
Technology Solutions for Data Sovereignty
Various technology solutions support the implementation of data sovereignty. These include cloud service providers that offer localized data centers, encryption tools for data protection, access management systems, and data loss prevention solutions. Organizations must evaluate these options and select those that align with their data sovereignty requirements.
Overcoming Data Sovereignty Challenges
While data sovereignty offers numerous benefits, it also presents challenges that organizations must navigate to ensure a balance between data accessibility and sovereignty.
Balancing Data Accessibility and Sovereignty
Organizations should strive to strike a balance between data accessibility for authorized users and the need to maintain data sovereignty. This involves implementing robust access control mechanisms, strong encryption protocols, and secure data sharing frameworks.
Addressing Cross-Border Data Transfer Issues
Cross-border data transfers are a major challenge in data sovereignty. Organizations need to identify and comply with data protection requirements in different jurisdictions, establish data transfer agreements, and implement secure data transfer mechanisms, such as encryption and secure file transfer protocols. This ensures that data remains protected during transit and satisfies local regulations.
Kiteworks Helps Organizations Achieve and Maintain Data Sovereignty
Data sovereignty is a critical element in the digital economy, and organizations must adhere to best practices to ensure the protection and control of their data. By understanding the definition, importance, legal landscape, key principles, implementation strategies, and challenges of data sovereignty, organizations can develop comprehensive solutions that enable them to operate efficiently and comply with regulatory requirements. Data sovereignty is an ongoing journey that requires continuous adaptation to evolving regulations and technologies to maintain the trust and confidence of consumers and stakeholders.
The Kiteworks Private Content Network, a FIPS 140-2 Level 1 validated secure file sharing and file transfer platform, consolidates email, file sharing, web forms, SFTP and managed file transfer, so organizations control, protect, and track every file as it enters and exits the organization.
Kiteworks plays a crucial role in businesses’ data sovereignty efforts. For example, Kiteworks’ encryption and access control features protect personal information during cross-border transfers, ensuring secure transmission.
Kiteworks’ extensive deployment options, including private, hybrid, and FedRAMP virtual private cloud, can be configured to store data in specific geographic locations. By storing data in specific locations, organizations can ensure that they are adhering to the data sovereignty laws of the countries in which they operate.
Kiteworks also supports data portability requirements by enabling users to securely access, transfer, and download their personal information. Kiteworks also provides organizations with the ability to establish opt-in mechanisms and procedures for data collection, detailed consent forms, and minor consent procedures. These features help organizations comply with consent requirements, which are a key aspect of data sovereignty.
Finally, Kiteworks’ detailed audit trail enables organizations to prove their compliance with data sovereignty laws to auditors.
With Kiteworks: control access to sensitive content; protect it when it’s shared externally using automated end-to-end encryption, multi-factor authentication, and security infrastructure integrations; see, track, and report all file activity, namely who sends what to whom, when, and how.
Finally demonstrate compliance with regulations and standards like GDPR, HIPAA, CMMC, Cyber Essentials Plus, IRAP, and many more.
To learn more about Kiteworks, schedule a custom demo today.
Additional Resources
- Brief Expand Visibility and Automate Protection of All Sensitive Email
- Brief Navigate the Digital Trifecta of Data Sovereignty, Cybersecurity, and Compliance With Kiteworks
- Blog Post Data Sovereignty and GDPR [Understanding Data Security]
- Video What Is Email Security? How to Protect Your Sensitive Content With Email Security
- Brief Secure Protocol Package: Strengthening Data Exchange With SFTP and SMTP