PCI DSS Compliance Challenges
Achieving PCI DSS compliance for businesses requires implementing and maintaining extensive security controls, protecting stored and transmitted cardholder data, restricting access to sensitive information, and regularly monitoring and testing security systems to identify potential vulnerabilities. PCI DSS v4.0, the latest version of the standard, introduces new requirements and updates existing ones from version 3.2.1. Organizations must implement these changes by March 2025.
Secure Network and Systems
PCI DSS compliance requires organizations to establish and maintain a secure network by installing and configuring firewalls, using strong passwords, protecting against malware, and developing secure systems and applications. Implementing these controls can be complex and resource-intensive, requiring significant investments in technology, expertise, and ongoing maintenance. Organizations must also ensure that their systems and processes are regularly updated to address emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
Data Protection and Asset Control
Protecting sensitive cardholder data is the fundamental aim of PCI DSS compliance for businesses. These organizations must encrypt stored data, secure transmitted data, restrict access to authorized personnel, assign unique user IDs, and control physical access to data centers. Implementing and managing these data protection measures can be challenging, particularly for organizations with complex IT environments and diverse user populations. Ensuring that all data is properly secured and that access controls are consistently enforced requires rigorous processes and ongoing vigilance.

Monitor, Test, and Policy Maintenance
Monitoring, testing, and maintaining policies are essential for identifying potential security gaps and fostering a culture of security awareness, as well as, inevitably, demonstrating PCI DSS compliance. Organizations must use audit logs to track and monitor access to cardholder data, regularly test security systems and processes, and maintain comprehensive information security policies. Implementing these measures can be time-consuming and resource-intensive, requiring specialized expertise and tools. Organizations must also ensure that their monitoring and testing processes are effective in detecting and responding to potential security incidents.
PCI DSS Compliant File Sharing

Hardened Virtual Appliance Secures Data
Kiteworks addresses the challenges of establishing a secure network by leveraging AWS and utilizing single-tenant private clouds to protect cardholder data. The platform operates on a least-privilege default, ensuring that only necessary traffic is permitted, and all connectivity is through secure, encrypted channels. Kiteworks is a pre-hardened appliance, and antivirus and vulnerability mitigation are deployed to all servers. These features collectively create a strong security foundation for the Kiteworks platform.
Controls and Robust Encryption Protect Assets
Kiteworks ensures the protection of sensitive cardholder data by encrypting data at rest with AES-256 and data in transit with TLS 1.3. Customers are responsible for managing their own encryption keys, providing an additional layer of security. Access to sensitive data is controlled by customers through built-in authentication, integration with existing identity providers, and granular access controls. Each user account is assigned a unique ID, and the customer configures password security requirements. These features ensure that sensitive data remains secure and accessible only to authorized personnel.
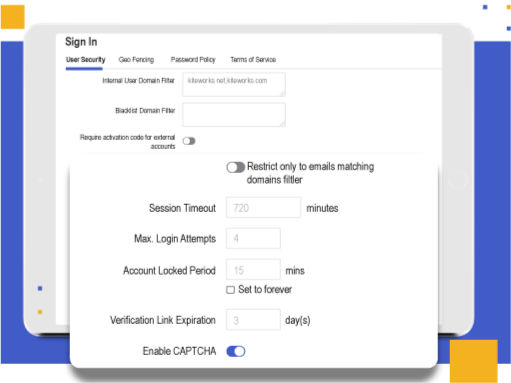
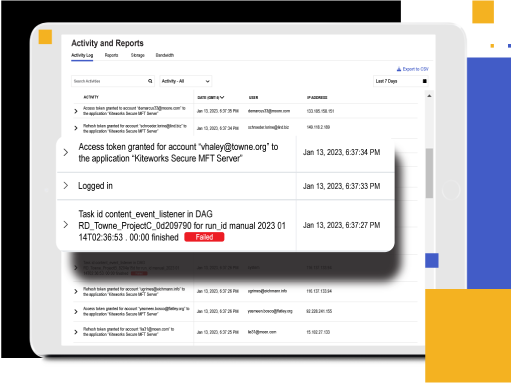
Real-time Monitoring Identifies Gaps
Kiteworks supports ongoing monitoring, testing, and policy enforcement by providing SIEM integration and log forwarding. Audit logs capture all user access, changes to accounts, and authentication settings in real time, with log files made immutable by design. The platform also manages vulnerability scans, bounty programs, and third-party penetration tests, which are conducted regularly. These features help organizations stay vigilant, identify potential security gaps, and foster a culture of security awareness and responsibility among employees, ensuring continuous compliance with PCI DSS requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions
All entities involved in processing, storing, or transmitting credit card information, merchants, payment processors, acquirers, issuers, and service providers, must comply with PCI DSS. PCI DSS compliance is mandatory for organizations handling payment card data globally, regardless of the country they operate in. While PCI DSS is not a legal requirement enforced by governments, it is a contractual obligation for businesses that accept payment cards.
PCI DSS affects a wide range of industries that handle credit card transactions, including retail, hospitality, e-commerce, financial services, and healthcare. Any business that accepts, processes, stores, or transmits credit card data must comply with PCI DSS, regardless of their size or the number of transactions they process. This includes both brick-and-mortar and online businesses across various sectors.
The key PCI DSS v4.0 requirements include installing and maintaining network security controls, protecting stored account data and cardholder data during transmission, protecting systems from malicious software, developing secure systems and software, restricting access, identifying users, authenticating access, logging and monitoring, testing security, and supporting information security with organizational policies and programs.
Noncompliance with PCI DSS can result in hefty fines, increased transaction fees, damage to reputation, and even the loss of the ability to process credit card payments. These fines can range from $5,000 to $100,000 per month, depending on the size of the company and the duration of noncompliance.
The purpose of PCI DSS compliance for businesses is to establish a global standard for securing credit card transactions and protecting cardholder data from theft and fraud. By adhering to PCI DSS requirements, businesses can minimize the risk of data breaches, maintain customer trust, and avoid costly penalties and reputational damage associated with noncompliance and security incidents.
FEATURED RESOURCES

Kiteworks Introduces Next-Generation Digital Rights Management

Kiteworks Private Content Network in the Compliance Era

Unlock Zero Trust at the Content Layer With Kiteworks and Forcepoint

Master Digital Rights Management: 2023 Sensitive Content Communications Report

