
Data Security and Compliance Insights from IBM’s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report
Cost of Data Breaches Spike 10% in Past Year
IBM’s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report sheds light on the escalating financial and reputational impacts of data breaches, providing critical insights for businesses worldwide. As cyber threats continue to evolve, the report reveals a troubling rise in breach costs, which spiked 10% year over year, driven by factors such as shadow data, the increasing integration of Generative AI (GenAI) in business processes, and the growing complexity of managing sensitive content across multiple platforms. These findings underscore the urgent need for organizations to adopt robust data security measures to protect their assets and ensure regulatory compliance.
The report highlights the proliferation of shadow data—unmanaged, unstructured data stored in various locations—poses a significant challenge, contributing to longer breach life cycles and higher costs. At the same time, the integration of GenAI introduces new vulnerabilities, as compromised AI models can lead to unintentional exposure of sensitive information. With personal data breaches accounting for nearly half (46%) of all incidents, businesses must prioritize the protection of customer data to avoid severe financial penalties and loss of consumer trust.
Kiteworks offers comprehensive solutions to address these pressing issues, providing organizations with the tools they need to secure sensitive data, manage compliance requirements, and mitigate the risks associated with modern cyber threats. By leveraging Kiteworks’ advanced security features and hardened virtual appliance, businesses can reduce the likelihood of data breaches, protect their brand reputation, and achieve long-term operational resilience.
Proliferation of Shadow Data and Its Impact on Breach Costs
The concept of shadow data has emerged as a critical concern in today’s digital landscape, particularly given its significant role in data breaches.
What Is Shadow Data?
Shadow data refers to unmanaged and often untracked data that is stored in various locations across an organization’s network. This data typically exists outside the formal data management policies and oversight, making it particularly vulnerable to breaches. Alarmingly, IBM found that one in three (35%) data breaches now involve shadow data, highlighting the widespread nature of this issue. Further, shadow theft correlates to a 16% greater cost of a breach. The 2024 Kiteworks Sensitive Content Communications Privacy and Compliance Report underscores the severity of this challenge, revealing that 57% of organizations are unable to track, control, or report on external content sends and shares. This lack of oversight presents substantial governance risks, as it increases the potential for data to be compromised without the organization’s knowledge.
Challenges of Managing Shadow Data
Managing shadow data is fraught with challenges, primarily due to its unstructured nature and the multiple environments in which it resides, such as cloud and on-premises systems. The dispersed nature of shadow data makes it difficult to secure, track, and control, leading to extended breach life cycles. According to the IMB report, data breaches involving shadow data take 26.2% longer to identify and contain, exacerbating their impact on organizations. This extended timeline not only increases the financial cost of a breach but also amplifies the potential for regulatory penalties and damage to an organization’s reputation.
Security and Compliance Risks of Compromised GenAI Data
As Generative AI (GenAI) continues to revolutionize industries, its integration into business processes has brought about both opportunities and challenges. Organizations across sectors are leveraging GenAI for various applications, from customer service automation to advanced data analytics. However, with this rapid adoption comes significant security and compliance risks, particularly when sensitive data is involved.
Growing Use of GenAI in Business
GenAI is being embraced at an unprecedented rate, with businesses increasingly relying on it to enhance efficiency, drive innovation, and gain a competitive edge. Whether it’s through chatbots, predictive analytics, or content generation, GenAI tools are becoming integral to daily operations. However, the deployment of these AI models often involves processing large amounts of sensitive data, including personally identifiable information (PII), proprietary business information, and even financial records.
The security implications of this trend cannot be overstated. According to the Kiteworks 2024 Sensitive Content Communications Privacy and Compliance Report, 39% of respondents identified the potential leak of sensitive data as a top risk associated with the use of public GenAI tools. This concern is well-founded, given that GenAI models can be vulnerable to various types of attacks and data exposures. As organizations integrate AI more deeply into their operations, they must also contend with the growing complexity of ensuring that these systems are secure and compliant with data protection regulations.
Risks Associated with Compromised GenAI Data
The risks posed by compromised GenAI data are multifaceted. One of the primary concerns is the possibility of data poisoning, where malicious actors intentionally introduce false or misleading data into the AI training process. This can lead to skewed outputs, incorrect decision-making, and potentially catastrophic outcomes for businesses. Additionally, GenAI models are susceptible to model extraction attacks, where adversaries can reverse-engineer the model to gain access to the underlying data and intellectual property.
Another significant risk is the inadvertent exposure of sensitive data through AI-driven applications. For example, if a GenAI model is trained on unclassified or poorly secured data, there is a heightened risk that sensitive information could be leaked or mishandled. This is particularly concerning in industries like healthcare and finance, where data breaches can result in severe regulatory penalties and loss of consumer trust.
Moreover, as AI models are increasingly deployed in cloud environments, they become targets for sophisticated cyberattacks. Attackers may exploit vulnerabilities in cloud infrastructure or intercept data during transmission, leading to unauthorized access and data breaches. Given these risks, it is imperative for organizations to implement robust security measures tailored specifically to the unique challenges posed by GenAI.
KEY TAKEAWAYS

KEY TAKEAWAYS
- Shifting Data Breach Trends:
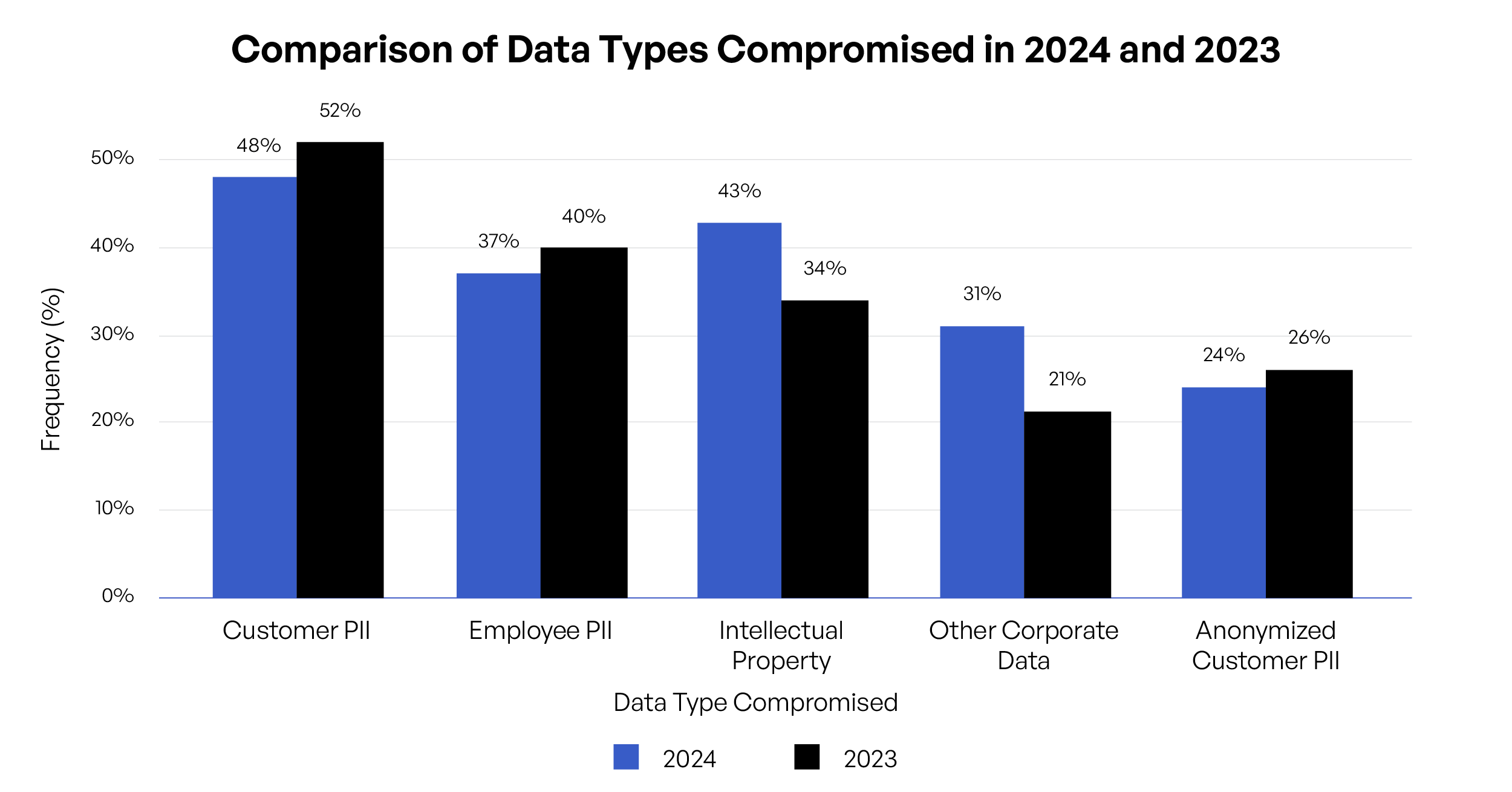
The frequency of data types compromised is changing, with Intellectual Property breaches rising from 34% in 2023 to 43% in 2024. This highlights the increasing value and targeting of proprietary information by cybercriminals. - Decline in PII Compromise:
While Customer PII remains a major target, its compromise rate decreased slightly from 52% in 2023 to 48% in 2024. This may indicate improvements in data protection measures, but the threat remains significant. - Rising Costs of Data Breaches:
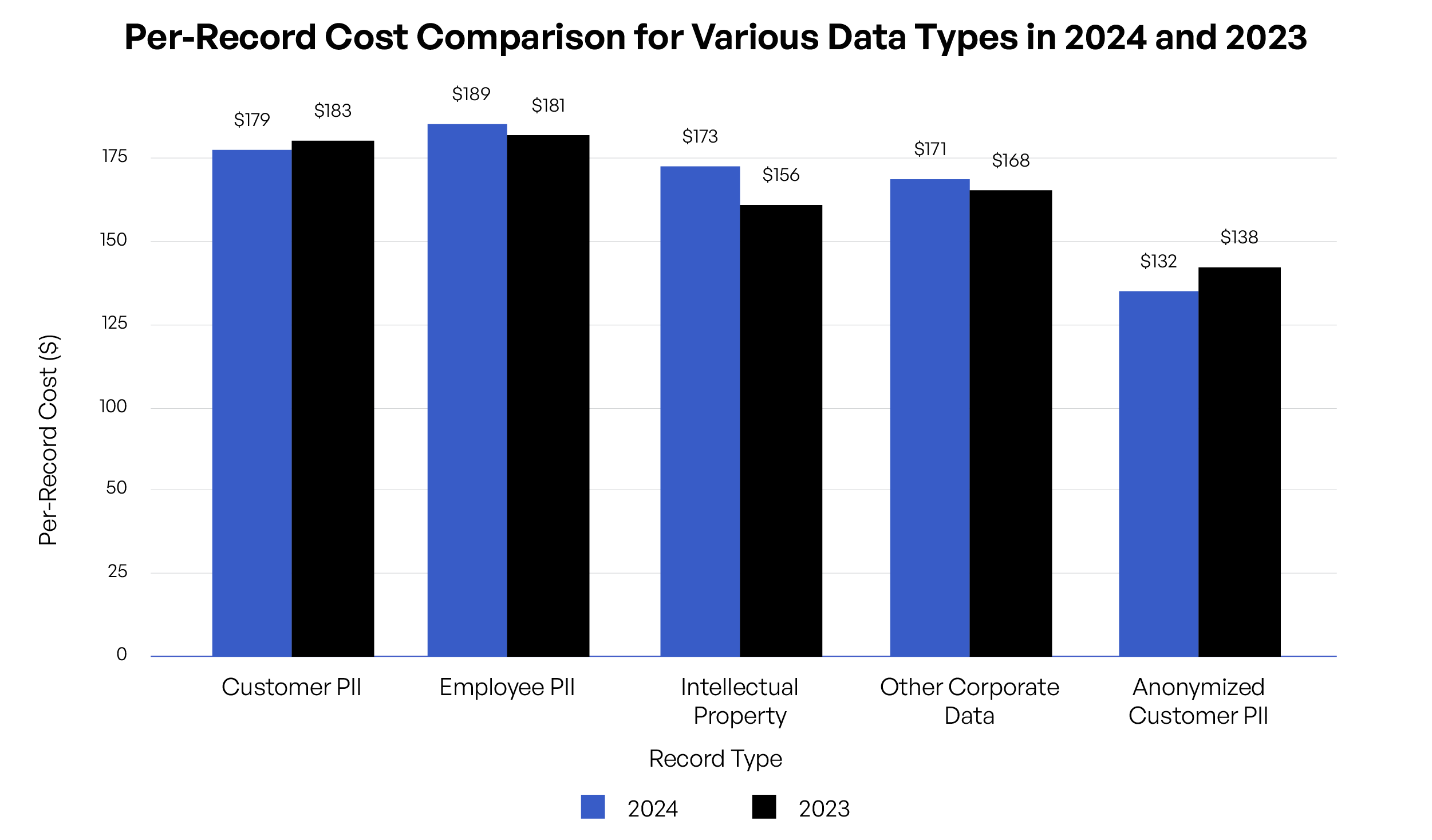
The per-record cost of Intellectual Property has surged from $156 in 2023 to $173 in 2024. Organizations must recognize the growing financial impact of breaches, particularly on sensitive corporate data. - Operational Data at Risk:
The cost associated with Other Corporate Data breaches has increased, reflecting a shift in cybercriminals’ focus towards broader corporate targets. This trend underscores the need for comprehensive data protection strategies. - The Challenge of Anonymized Data:
The cost per record for Anonymized Customer PII remains substantial, though slightly lower than in 2023. This suggests that even anonymized data is not immune to breaches, requiring continued vigilance in data handling practices.
What Is Needed to Secure GenAI Data
To effectively secure GenAI data, organizations must adopt a comprehensive data security framework that addresses the specific vulnerabilities associated with AI technologies. Kiteworks enables organizations to protect sensitive data used in GenAI applications. A key component of this framework is AI governance, which involves the implementation of policies and controls to manage the development, deployment, and use of AI models. This includes ensuring that data used in training AI models is properly classified, encrypted, and monitored throughout its life cycle. Kiteworks provides tools that enable organizations to maintain strict oversight of AI data pipelines, reducing the risk of data leakage and unauthorized access.
In addition to governance, compliance assurance is critical in securing GenAI data. As regulatory bodies increasingly scrutinize AI technologies, organizations must ensure that their AI deployments adhere to relevant data protection standards and regulations. Kiteworks’ compliance management features help organizations navigate the complex landscape of AI regulation, providing the necessary tools to document and demonstrate compliance with laws such as GDPR, CCPA, and HIPAA.
Finally, real-time monitoring and threat detection are essential for mitigating the risks associated with GenAI. Kiteworks offers advanced monitoring capabilities that allow organizations to detect and respond to potential security incidents involving AI data. By continuously analyzing AI model outputs and data flows, businesses can identify anomalies and address vulnerabilities before they lead to data breaches.
Addressing the High Incidence of Personal Data Breaches
Personal data breaches have become a significant concern for organizations across all sectors and comprise 46% of all data breaches. These breaches, which often involve the exposure of customer personally identifiable information (PII), pose serious financial, legal, and reputational risks. As businesses increasingly engage with third parties and expand their digital ecosystems, the incidence of personal data breaches continues to rise, making it imperative for organizations to implement robust security measures to protect sensitive information.
Data Types Compromised: 2024 vs. 2023
Prevalence of Personal Data Breaches
The financial and reputational impact of personal data breaches can be devastating for businesses. When PII is compromised, organizations may face significant financial penalties, class-action lawsuits, and loss of consumer trust. The 2024 Kiteworks Sensitive Content Communications Privacy and Compliance Report highlights that 66% of organizations exchange sensitive content with over 1,000 third parties, further increasing the risk of PII breaches. Each time data is shared with an external party, the potential for a breach multiplies, underscoring the need for stringent data protection protocols.
Why Personal Data Breaches Are So Costly
Personal data breaches are among the most expensive types of data breaches an organization can experience. The high cost per record of compromised personal data is driven by several factors. First, the regulatory environment around PII is stringent, with laws like GDPR, HIPAA, and U.S. state data privacy laws like CCPA imposing heavy fines for non-compliance. These regulations not only mandate strict data protection measures but also require organizations to notify affected individuals and authorities in the event of a breach, which can be a costly process.
In addition to regulatory fines, organizations that suffer personal data breaches often incur significant litigation costs. According to the Kiteworks report, half of the respondents who exchanged sensitive content with 5,000 or more third parties spent over $5 million in annual litigation costs last year. These costs include legal fees, settlements, and the expenses associated with defending against lawsuits. Furthermore, the reputational damage caused by a personal data breach can lead to lost business, as customers may lose trust in the organization’s ability to protect their information.
Protecting Personal Data with Advanced Security and Compliance
To mitigate the risks associated with personal data breaches, organizations must adopt advanced security measures and ensure compliance with data protection regulations.
Encryption and Access Control: Robust encryption and access control mechanisms to ensure that personal data is protected both at rest and in transit. By encrypting data, organizations can prevent unauthorized access, even if data is intercepted or stolen. Access control features ensure that only authorized individuals can view or modify sensitive information, reducing the risk of internal threats.
Compliance Management: With Kiteworks, organizations can effectively track data use and ensure compliance with various data protection regulations, including GDPR, HIPAA, and individual state data privacy regulations like CCPA. The platform’s compliance management tools help organizations maintain detailed records of data processing activities, making it easier to demonstrate compliance during audits or in the event of a data breach.
AI-Enabled Incident Response: In the unfortunate event of a data breach, AI-enabled incident response becomes crucial for faster identification and containment, significantly minimizing the overall impact on the organization. Leveraging AI, the platform’s incident response features empower organizations to swiftly detect breaches, accurately assess the extent of the compromise, and execute the most effective actions to mitigate damage.
Types of Data at Risk: Understanding the Breach Landscape
The IBM report provides valuable insights into the types of data most frequently targeted in breaches. Understanding these categories is crucial for organizations to prioritize their data protection efforts effectively.
Customer PII
Customer PII remains the most breached type of record, involved in 48% of all breaches (down from 52% in 2023). This category includes names, email addresses, phone numbers, and other personal details. Protecting customer PII is paramount as its compromise can lead to identity theft, financial fraud, and severe reputational damage for the organization. Moreover, the loss of customer PII often results in the highest per-record cost, making it a critical focus for data security efforts.
Employee PII
Employee PII was the second most common type of breached record, implicated in 37% of incidents (down from 40% last year). This data includes personal information about an organization’s workforce. Protecting employee PII is not only a legal and ethical obligation but also crucial for maintaining trust within the organization and preventing internal fraud or social engineering attacks targeting employees.
Intellectual Property
Intellectual property, which includes trade secrets, proprietary algorithms, and innovative designs, was involved in 43% of breaches (up from 34% last year), representing a significant threat to an organization’s competitive advantage and future revenue streams. Other corporate data breaches were also up, from 21% to 31%. These jumps are concerning with malicious nation-state attacks on corporate IP and other types of secret information on the upswing. In addition, loss of intellectual property can have long-lasting impacts on a company’s market position and financial health, making its protection a strategic imperative.
Anonymized Customer Data
Other corporate data breaches were also up—from 21% to 31% over the previous year. While this data is intended to protect individual privacy, its compromise can still pose risks if de-anonymization techniques are applied. Organizations must ensure robust anonymization processes and treat this data with the same level of security as identifiable information to maintain customer trust and comply with data protection regulations.
By understanding these different types of data at risk, organizations can tailor their security strategies to provide comprehensive protection across all data categories. Implementing strong encryption, access controls, and monitoring systems for each data type is essential in building a resilient defense against the ever-evolving threat landscape.
Cost Per Data Record Breached
Importance of a Comprehensive Data Security Strategy
In an era where cyber threats are becoming increasingly sophisticated, a comprehensive data security strategy is no longer optional—it is essential for safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring organizational resilience. To effectively counter these evolving risks, businesses must adopt a multi-layered approach that addresses every aspect of their data security framework. This strategy not only protects against immediate threats but also positions organizations to respond swiftly and effectively in the event of a breach.
Lessons from the Cost of Data Breach Report
The IBM 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report offers several key findings that underscore the need for proactive data security measures. One of the most striking revelations is the growing cost of data breaches, with the average cost now exceeding previous years. The report also emphasizes the critical role of AI and automation in reducing these costs. Organizations that leverage AI-driven security tools tend to identify and contain breaches more quickly, significantly lowering the financial and operational impacts.
AI and automation not only expedite breach detection but also improve response times, enabling organizations to mitigate damage more effectively. The report makes it clear that businesses without these advanced technologies are at a considerable disadvantage, facing longer breach life cycles and higher associated costs. These findings highlight the urgency for companies to integrate AI and automation into their data security strategies to protect their assets and reduce vulnerabilities.
Implementing Best Practices with Kiteworks
To address these challenges, Kiteworks provides a comprehensive suite of tools designed to fortify data security across all aspects of an organization’s operations.
Hardened and Integrated Security: Kiteworks offers a robust platform that integrates various advanced security solutions into a hardened virtual appliance. This integration allows organizations to manage all aspects of their data security from one central location, enhancing visibility and control. By providing tools for encryption, access control, and threat detection, Kiteworks ensures that sensitive data is protected at every stage of its life cycle.
Demonstrate Compliance: Kiteworks enables organizations to demonstrate compliance by providing a secure platform for managing sensitive content communications with advanced governance and control features. The platform ensures that all data transfers, whether internal or external, are fully encrypted and tracked, offering detailed audit logs and reporting capabilities to meet regulatory requirements. Plus, by centralizing the management of sensitive information, Kiteworks helps organizations mitigate risks and confidently demonstrate compliance during audits and assessments.
Continuous Improvement: In the face of constantly evolving threats, maintaining a static security posture is not enough. Kiteworks helps organizations stay ahead of these threats by continuously updating its security protocols and tools. This commitment to continuous improvement ensures that businesses are always equipped with the latest defenses against emerging cyber threats. By regularly enhancing its platform’s capabilities, Kiteworks enables organizations to protect their sensitive data more effectively and respond to new challenges as they arise.
Conclusion: Why Robust Data Security Is Essential
The landscape of cyber threats is growing more complex and dangerous, making robust data security solutions an absolute necessity for businesses of all sizes. The rising costs associated with data breaches, coupled with the increasing frequency of incidents involving shadow data, GenAI, and personal information, underscore the urgency for organizations to strengthen their security measures.
Considering these growing threats, it is imperative that businesses take proactive steps to safeguard their sensitive data. Investing in comprehensive security platforms like Kiteworks is not just a strategic choice but a critical action that can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches. Kiteworks provides a suite of advanced tools designed to address the multifaceted challenges of modern cybersecurity, from securing unstructured data and managing compliance to leveraging AI for enhanced incident response.
By adopting a proactive approach to data security, organizations can protect their assets, maintain regulatory compliance, and preserve their reputation in an increasingly digital world. The time to act is now—before the next breach occurs. With the right solutions in place, businesses can navigate the complexities of today’s cybersecurity landscape with confidence, ensuring their long-term success and resilience.
FAQs
According to the IBM report, the cost of data breaches spiked 10% year over year. This significant increase underscores the growing financial impact of cyber threats on businesses worldwide.
The report found that one in three (35%) data breaches now involve shadow data. Additionally, shadow theft correlates to a 16% greater cost of a breach, highlighting the financial impact of this issue.
Data breaches involving shadow data take 26.2% longer to identify and contain, according to the IBM report. This extended timeline not only increases the financial cost of a breach but also amplifies the potential for regulatory penalties and reputational damage.
The report indicates that personal data breaches account for nearly half (46%) of all incidents. This high proportion emphasizes the critical need for businesses to prioritize the protection of customer personally identifiable information (PII).
The IBM report emphasizes that organizations leveraging AI-driven security tools tend to identify and contain breaches more quickly, significantly lowering the financial and operational impacts. Businesses without these advanced technologies face longer breach life cycles and higher associated costs.
Additional Resources