
Data Privacy Advantage: How Strong Data Governance Builds Trust in 2025
In a world where data breaches regularly make headlines and regulations multiply across jurisdictions, organizations face mounting pressure to safeguard information while driving innovation. The recent Cisco 2025 Data Privacy Benchmark Study reveals compelling insights into how leading companies are balancing these priorities—and reaping substantial rewards in the process.
The Data Localization Paradox
Organizations today face an intriguing contradiction. According to Cisco’s research, 90% of respondents believe data would be inherently safer when stored within their own country or region. Yet simultaneously, 91% trust global providers to better protect their data than local alternatives—a 5% increase from last year.
This apparent disconnect makes perfect sense in context. Data privacy is core to trust and a competitive differentiator in today’s digital economy. Organizations want both the assurance of local data storage and the sophisticated security infrastructure that global providers deliver. The challenge? Data localization comes at a cost. Eighty-eight percent of respondents acknowledge significant operational expenses associated with localization requirements. These costs create a tangible tension between regulatory compliance and operational efficiency.
Cross-Border Data Flows and Economic Growth
Despite the trend toward localization, there’s growing recognition of the economic benefits of secure cross-border data flows. The study found that 85% of respondents believe “Data Free Flow with Trust” initiatives can boost economic growth. This aligns with efforts by organizations like the OECD, which has identified over 100 data localization requirements across 40 countries that potentially fragment the digital economy.
Initiatives such as the G20’s Data Free Flow with Trust, the Global Cross-Border Privacy Rules Forum, and the EU-UK Trade and Cooperation Agreement aim to make national data governance systems interoperable while maintaining appropriate safeguards. These frameworks seek the balance that organizations crave: data protection with minimal barriers to innovation and commerce.
The challenge for multinational organizations lies in navigating this complex landscape while maintaining consistent security standards. Global providers with local infrastructure offer a compelling solution—they combine worldwide expertise with regional compliance capabilities. This approach explains why trust in global providers remains consistently high across all surveyed countries, despite varying regulatory approaches.
Privacy Regulation as a Trust Accelerator
Far from viewing regulation as a burden, 86% of organizations report that privacy laws have positively impacted their operations—up from 80% in 2024. This perspective shift underscores how compliance has evolved from checkbox exercise to strategic advantage.
The benefits materialize in consumer confidence. For the first time since Cisco began tracking in 2019, a majority of global consumers (53%) report awareness of their country’s privacy laws. Notably, 81% of these aware consumers feel empowered to protect their personal data, compared to just 44% among those unfamiliar with privacy regulations.
This correlation between regulatory awareness and consumer confidence creates a compelling case for transparent privacy practices. Organizations that clearly communicate their compliance efforts convert regulatory obligations into trust-building opportunities.
Regional Variations in Privacy Awareness
The study reveals fascinating geographic differences in privacy regulation awareness. China (81%), France (73%), and Mexico (66%) show the highest consumer awareness of privacy laws, while Australia (26%), India (37%), and Germany (48%) display lower awareness levels.
These variations highlight opportunities for organizations to differentiate themselves through privacy education and transparency, particularly in markets where consumer awareness remains developing. Companies that proactively communicate their privacy practices can stand out in less privacy-mature markets.
The regional variations also reflect different regulatory approaches and implementation timelines. Countries with recent high-profile legislation or enforcement actions tend to show greater public awareness. Organizations operating across multiple jurisdictions must calibrate their privacy communications to these varying awareness levels, emphasizing different aspects of their privacy programs depending on regional contexts.
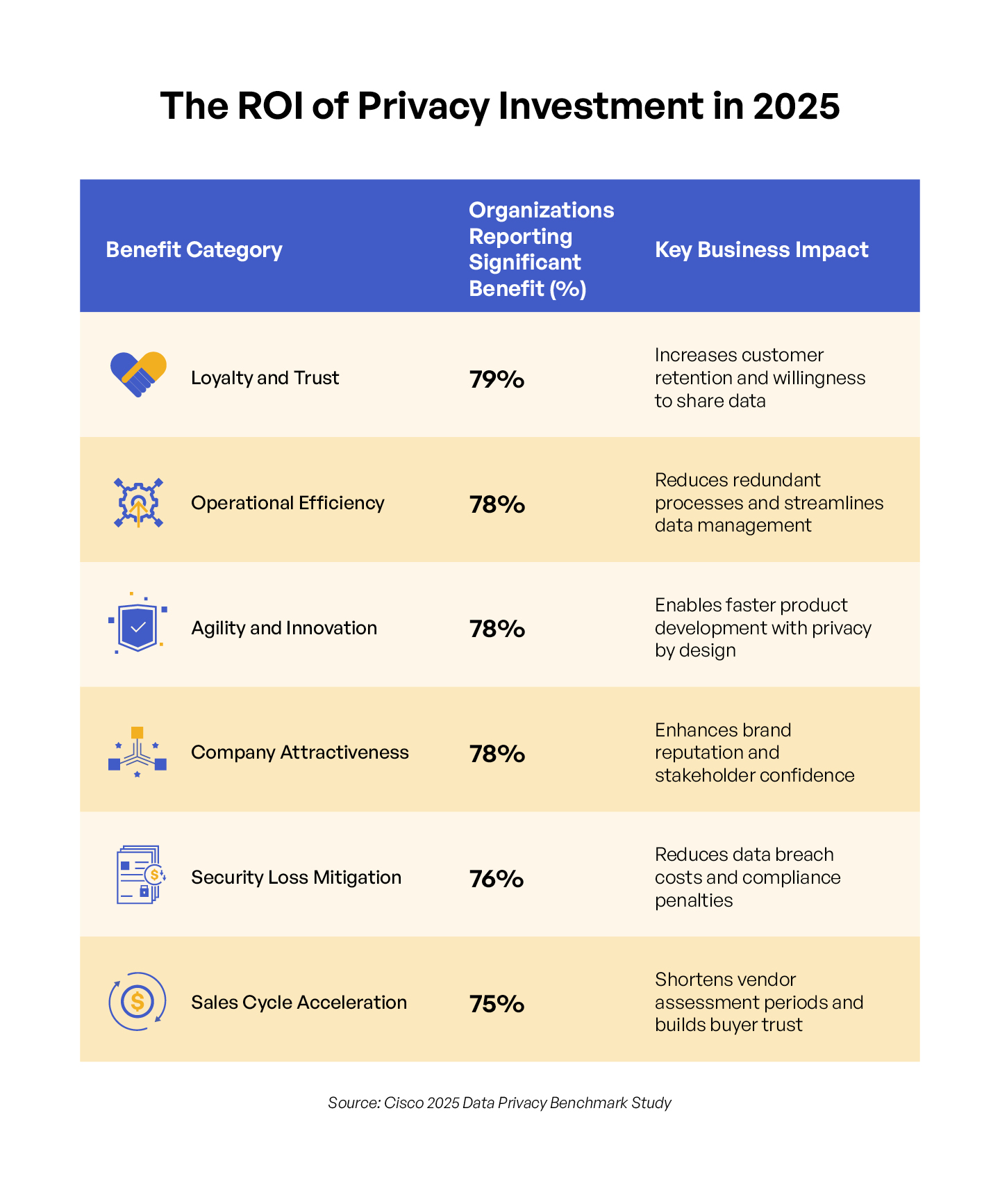
ROI of Privacy Investment
Despite compliance costs, organizations overwhelmingly recognize the value proposition. An impressive 96% of respondents believe privacy investment benefits outweigh associated costs—with the median organization reporting a 1.6x return on investment.
The payoff manifests across multiple dimensions. Enhanced loyalty and trust with customers leads the pack at 79%, followed closely by improved operational efficiency, increased agility and innovation, and enhanced company attractiveness—all at 78%. Organizations also report reduced security losses (76%) and fewer sales delays (75%). This comprehensive set of benefits demonstrates how privacy investments deliver value beyond mere regulatory compliance.
These benefits create a virtuous cycle. As Dev Stahlkopf, Cisco’s Executive Vice President and Chief Legal Officer explains, “For organizations working toward AI readiness, investing in privacy establishes essential groundwork, helping to accelerate effective AI governance.”
Sustained Investment Across Organizations
Privacy spending has remained consistent over the past four years, averaging $2.7 million across surveyed organizations. Medium to large enterprises generally increased privacy budgets year-over-year, while smaller organizations (50-249 employees) reduced spending. This divergence suggests that larger organizations may be finding economies of scale or competitive advantages from privacy investments that smaller entities haven’t yet realized.
The spending patterns also reflect different maturity levels in privacy programs. Organizations with established programs can focus investments on optimization and innovation, while those in earlier stages must concentrate on foundational compliance infrastructure. As privacy programs mature, their strategic value increases—explaining why larger organizations continue to expand investments despite having already established basic compliance capabilities.
External validation continues to play a critical role, with 99% of respondents emphasizing the importance of privacy certifications when selecting vendors—up from 98% last year. These third-party validations provide objective evidence of privacy commitments, reducing the due diligence burden on organizations. They also facilitate trust in business relationships, particularly important in data-intensive partnerships where privacy concerns might otherwise create friction.
Best Practices for Building a Strong Data Governance Program
A strong data governance program is essential for protecting sensitive data and maintaining stakeholder trust. Effective governance ensures data integrity, security, and compliance while enabling organizations to make informed decisions and reduce risk. By implementing structured policies and controls, businesses can safeguard critical assets, prevent data breaches, and foster a culture of accountability.
The following best practices will help you build a robust data governance program that strengthens security, enhances regulatory compliance, and instills confidence among stakeholders.
Establish Clear Data Ownership and Accountability
Assign data stewards responsible for maintaining data integrity, security, and compliance. Clear ownership ensures accountability, reducing risks of mismanagement while improving trust among stakeholders.
Classify and Label Sensitive Data
Implement a structured classification system to identify and label sensitive data based on risk levels. Proper classification enhances security controls, ensuring appropriate handling and compliance with regulations.
Implement Role-Based Access Controls (RBAC)
Restrict data access to authorized personnel based on roles and responsibilities. RBAC minimizes exposure to sensitive information, reducing insider threats and unauthorized data access risks.
Enforce Strong Data Encryption and Masking
Apply encryption for data at rest and in transit, and use masking techniques for non-production environments. Encryption safeguards against breaches, ensuring confidentiality and regulatory compliance.
Develop and Communicate Data Policies
Create clear, enforceable data governance policies covering data handling, retention, and security. Transparent policies build stakeholder confidence and provide a foundation for compliance and risk mitigation.
Continuously Monitor and Audit Data Usage
Deploy monitoring tools to track data access, modifications, and transfers. Regular audits help detect anomalies, prevent breaches, and demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements.
Integrate Data Governance with Security and Compliance Frameworks
Align governance policies with NIST, ISO 27001, GDPR, and other standards. Integrated frameworks ensure a holistic approach to data protection and regulatory adherence.
Educate and Train Employees on Data Governance
Conduct regular security awareness training sessions on data security best practices, regulatory requirements, and phishing awareness. A well-informed workforce reduces human errors and strengthens the organization’s data protection culture.
Implement Data Retention and Disposal Policies
Define and enforce policies for data retention and secure disposal of obsolete information. Effective lifecycle management minimizes data exposure risks and ensures compliance with legal requirements.
Leverage AI and Automation for Data Protection
Utilize AI-driven security tools to detect anomalies, enforce policies, and prevent data leaks. Automation enhances efficiency, reduces manual errors, and strengthens proactive data protection efforts.
Navigating the GenAI Revolution
As generative AI adoption accelerates, privacy considerations take on heightened importance. The study reveals increasing comfort with these technologies—63% of respondents report high familiarity with GenAI (up from 55% in 2023), and 48% derive significant value from implementations (up from 37%).
Yet concerns persist. While worries about legal risks have decreased (69% to 55% year-over-year), substantial majorities still express concern about inaccurate outputs (67%), sensitive information exposure (64%), potential negative societal impacts (62%), and job displacement. This mixed picture reflects an evolving understanding of GenAI capabilities and limitations.
Notably, 90% of respondents recognize that strong privacy laws make customers more comfortable sharing data with AI applications. This highlights how robust privacy frameworks enable innovation by establishing necessary guardrails and building user confidence.
Organizations deploying GenAI face the challenge of balancing experimentation with risk management. Early adopters gain competitive advantages but must navigate uncertain regulatory territory and potential reputational risks. Privacy frameworks provide essential structure for this innovation process, helping organizations identify boundaries while maximizing value creation.

Data Input Challenge
The study reveals a concerning practice: despite growing awareness of AI risks, significant percentages of organizations report inputting sensitive information into GenAI applications. Nearly half (46%) input employee names or personal information, while 42% share non-public company information and 31% include customer names or information.
This gap between awareness and practice underscores the need for comprehensive AI governance policies that explicitly address data inputs and establish clear boundaries for responsible use. As organizations increasingly leverage GenAI for competitive advantage, establishing these guardrails becomes essential to mitigate privacy and security risks.
The challenge lies in developing policies that allow innovation while preventing sensitive data exposure. Organizations must educate users about appropriate data handling, implement technical safeguards, and establish clear accountability mechanisms. Success requires collaboration between privacy, security, legal, and business teams to develop practical guidelines that protect information without unnecessarily constraining legitimate business uses.
Balancing Resources in an AI-First World
The shift toward AI-centric operations is unmistakable. Nearly all respondents (99%) expect organizations to reallocate resources from privacy budgets to AI initiatives in the coming year. This reallocation reflects the growing strategic importance of AI capabilities.
However, AI governance delivers multifaceted benefits that complement privacy objectives. Building stakeholder trust stands out as the primary benefit, with 89% of respondents reporting moderate or significant advantages. Improvements in corporate values achievement, product quality enhancement, regulatory preparedness, and employee relations all follow closely behind, each at 85% or higher.
As organizations navigate this transition, maintaining privacy foundations remains essential. Rather than choosing between privacy and AI investments, forward-thinking organizations understand how privacy enables successful AI adoption by establishing the data governance foundations necessary for responsible implementation.
Integrating Privacy and AI Governance
The most successful organizations are finding ways to leverage existing privacy infrastructure to accelerate AI governance. Common elements between these disciplines include data mapping and classification, risk assessment frameworks, transparency requirements, rights management, and accountability mechanisms.
By building AI governance on these privacy foundations, organizations can accelerate responsible AI adoption while maintaining necessary protections. This integrated approach maximizes return on existing privacy investments while enabling AI innovation.
The Cisco 2024 AI Readiness Index reinforces this connection, finding that 98% of organizations feel increased urgency to invest in AI compared to the previous year, while only a small minority (13%) feel fully prepared to leverage AI’s potential. Organizations with mature privacy programs have a significant head start in this preparation, as they’ve already addressed many of the foundational data governance challenges that AI implementation requires.
Practical Steps for Privacy-Driven Organizations
Based on these findings, organizations seeking to maximize the privacy advantage should develop a strategic localization approach that balances regulatory requirements across jurisdictions while leveraging global providers’ security expertise. This means mapping data flows, understanding regional requirements, and creating a compliance architecture that minimizes fragmentation while meeting local obligations.
Organizations should also embrace privacy regulations as trust-building frameworks rather than compliance burdens, recognizing their role in boosting consumer confidence. This requires shifting from a minimalist compliance approach to proactive engagement with regulatory principles. By aligning privacy practices with regulatory expectations and communicating these efforts transparently, organizations transform compliance costs into relationship-building investments.
Measuring privacy ROI comprehensively represents another essential step. Beyond direct benefits like reduced breaches, organizations should track indirect advantages including improved innovation capabilities and enhanced reputation. This comprehensive view provides a more accurate picture of privacy’s strategic value and helps justify continued investment.
Implementing robust AI governance that builds upon existing privacy foundations allows organizations to mitigate risks while maximizing value. Rather than creating separate governance structures, integrating AI governance with privacy programs leverages existing expertise and processes while ensuring consistent approaches to data management.
Building a Foundation of Trust
As organizations navigate an increasingly complex regulatory landscape while pursuing AI-driven innovation, privacy investments deliver measurable returns. By approaching privacy as a strategic asset rather than a compliance cost, organizations establish the trust foundation necessary for sustainable growth.
The data is clear: organizations that prioritize privacy don’t just avoid penalties—they build stronger customer relationships, accelerate innovation, and position themselves for success in an AI-transformed landscape. In 2025 and beyond, the privacy advantage remains a powerful competitive differentiator for forward-thinking organizations.
Organizations that successfully integrate privacy, security, and AI governance create a unified approach to data stewardship that builds trust while enabling innovation. This holistic perspective transforms what could be competing priorities into complementary capabilities, positioning organizations to thrive in an increasingly data-driven economy.
FAQs
The Cisco study found that 96% of organizations believe privacy investment benefits outweigh costs, with a median 1.6x ROI. Key benefits include enhanced customer loyalty (79%), improved operational efficiency (78%), increased innovation (78%), and reduced security losses (76%).
Strong privacy laws significantly increase consumer confidence, with 81% of consumers who are aware of privacy regulations feeling empowered to protect their data, compared to just 44% of those unaware. This awareness creates a trust foundation that enables organizations to collect and use data more effectively.
Organizations face a paradox where 90% believe data is safer when stored locally, yet 91% trust global providers more than local alternatives. This reflects the desire for both regulatory compliance through local storage and access to sophisticated security infrastructure that global providers deliver.
Privacy investments establish the foundational data governance practices necessary for responsible AI implementation. Organizations are leveraging existing privacy infrastructure—including data mapping, risk assessment frameworks, and accountability mechanisms—to accelerate AI governance while maintaining appropriate protections.
Nearly all respondents (99%) expect resources to shift from privacy to AI in the coming year, reflecting AI’s strategic importance. However, successful organizations recognize that privacy and AI governance are complementary rather than competing priorities, with integrated approaches delivering the greatest business value.
Additional Resources
- Blog Post Zero Trust Architecture: Never Trust, Always Verify
- Video How Kiteworks Helps Advance the NSA’s Zero Trust at the Data Layer Model
- Blog Post What It Means to Extend Zero Trust to the Content Layer
- Blog Post Building Trust in Generative AI with a Zero Trust Approach
- Video Kiteworks + Forcepoint: Demonstrating Compliance and Zero Trust at the Content Layer

