An Overview of the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA)
The Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA) is comprehensive online consumer privacy legislation that was passed in March 2021. It seeks to provide consumers with added protection and control over their personal data. The act also helps protect businesses from potential liability, as it requires them to have robust safeguards in place to protect consumer data. There are noteworthy similarities and differences between VCDPA and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA). Read on for an in-depth review of the impact of the VCDPA on consumers and businesses, who must comply with the act and how they can do so, as well as an outline of the fines and penalties associated with the act.

What Is the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA)?
The Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA) is a comprehensive consumer data privacy law that was passed in March 2021 that provides consumers with greater control over their personal data. The act applies to any business that collects, uses, processes, transfers, or stores personal data from Virginia consumers. It establishes consumer protections, such as the right to access the personal data collected, the right to know the purposes for which it is used, and the right to request deletion of the data. The act requires businesses to have appropriate administrative, technical, and physical safeguards in place to protect consumer data.
What Are the Requirements of the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA)?
The VCDPA includes a number of requirements that businesses must abide by in order to comply with the act. Some of the main requirements of the act include:
- Establish a process to respond to consumer requests, such as requests for access to or deletion of their personal data;
- Designate a data protection officer to oversee the data processing activities of the business;
- Establish a privacy policy that clearly states how the business uses and protects consumer data;
- Notify consumers of any data breach or unauthorized access to their data;
- Implement appropriate technical and organizational measures to protect consumer data;
- Notify consumers when the business intends to use their data for other than the purpose for which the data was collected;
- Allow third-party providers access to consumer data only with the consumer’s consent;
- Obtain verifiable parental consent for the collection of personal data of children under the age of 13.
VCDPA vs. CCPA: What Are the Similarities and Differences?
The VCDPA and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) share many similarities. Both require businesses to provide data subject rights to consumers and to have appropriate administrative, technical, and physical safeguards in place to protect consumer data. Additionally, both acts require businesses to obtain parental consent for the collection of personal data of children under the age of 13.
However, there are some important differences between the two acts. Firstly, the CCPA applies to businesses that collect the personal data of California residents, while the VCDPA applies to businesses that collect the personal data of Virginia residents. Secondly, the CCPA has a broader definition of personal data, which includes biometric information, such as fingerprints and voice recordings, while the VCDPA does not. Thirdly, the CCPA levies a $2,500 fine for businesses found in violation of the act, and the VCDPA does not. Finally, the CCPA does not require businesses to designate a data protection officer, while the VCDPA does.
How Are Consumers Impacted by the VCDPA?
The VCDPA provides consumers with more control over their personal data. It gives them the right to access the personal data collected by businesses, to know the purposes for which their data is being used, and to request deletion of the data. The act requires businesses to obtain verifiable parental consent for the collection of personal data of children under the age of 13. These provisions help ensure that consumers have greater control over their personal data and that their data is used responsibly.
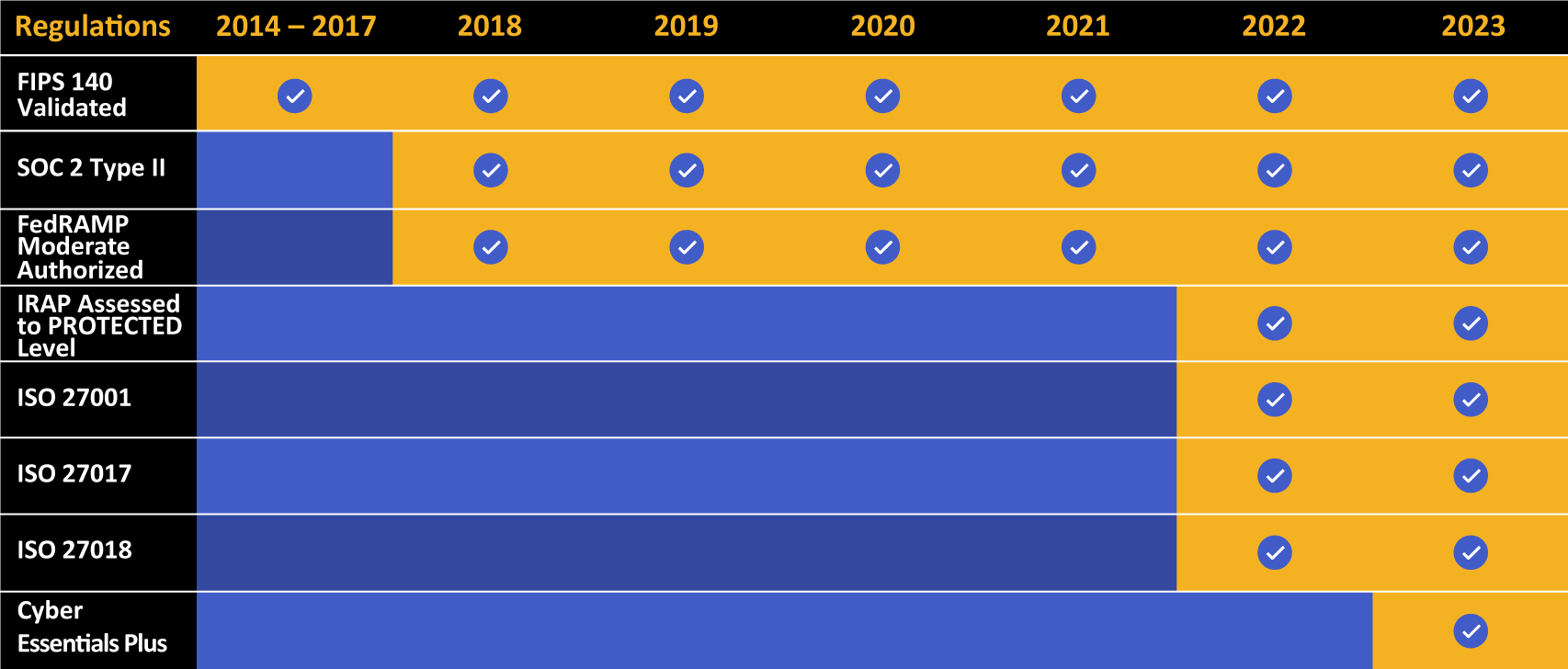
Kiteworks touts a long list of compliance and certification achievements.
How Are Businesses Impacted by the VCDPA?
The VCDPA has a significant impact on businesses that collect personal data from Virginia consumers. Firstly, it requires them to have robust administrative, technical, and physical safeguards in place to protect consumer data. The act requires businesses to respond to consumer requests for access to or deletion of their personal data. The VCDPA requires businesses to designate a data protection officer to oversee the data processing activities of the business. Businesses must invest time, money, and resources into complying with the act, as failure to do so can result in fines and penalties.
Who Must Comply With the VCDPA?
The Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA) is applicable to all entities that collect consumer data in the state of Virginia. This includes businesses such as telecommunications companies, banks and other financial institutions, retailers, online service providers, healthcare providers, and any other organization that collects and stores personal data obtained from Virginia consumers. All businesses that meet these criteria must comply with the VCDPA, which requires that they protect any consumer data they collect and use. Businesses must take appropriate security measures to protect the data, implement clear and understandable privacy policies, and provide consumers with the information they need to make informed decisions about how their data is used and shared.
How Can Businesses Comply With the VCDPA?
Businesses in Virginia must take several steps to comply with the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA). First, businesses must develop a privacy notice that explains their data collection, processing, and security practices. In addition, businesses must create a data security program that includes physical, technical, and administrative measures used to protect consumers’ data. Businesses must also assess the impacts of their data processing activities on the privacy and security of consumers’ data and take steps to mitigate them. Additionally, businesses need to maintain record keeping, reporting, and auditing mechanisms to ensure compliance with the law. Finally, businesses must take appropriate disciplinary action against their personnel for any violations of the VCDPA.
How Will the VCDPA Be Enforced?
The Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA) will be enforced by the Virginia Attorney General. The Attorney General will have the power to investigate violations of the act and enforce civil penalties for violations that are found to be intentional and willful. In addition to civil penalties, the Attorney General may also assess fines, issue cease and desist orders, and seek injunctive relief for any violations. In addition, the Attorney General may bring a civil action for any violations of the act. The VCDPA provides for a private right of action for any consumer affected by a violation of the act, allowing them to seek damages, attorneys’ fees, and other relief deemed appropriate by the court. These provisions are meant to help ensure that the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act is enforced and that companies handling consumer data act responsibly and in accordance with the law.
What Are the Fines and Penalties Under the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA)?
Businesses that fail to comply with the VCDPA can be subject to fines and penalties. The Virginia Attorney General can issue a civil penalty of up to $7,500 per violation, and if the violation is deemed to be willful or negligent, the penalty can be increased to up to $750,000. Finally, businesses that are found to have suffered a data breach due to a lack of adequate security measures can be subject to mandatory credit monitoring for affected consumers.
Final Thoughts on the Importance of the VCDPA
The Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act is an important piece of legislation that seeks to provide consumers with greater protection and control over their personal data. It also helps protect businesses from potential liability by requiring them to have appropriate safeguards in place to protect consumer data. By complying with the act, businesses can avoid costly fines and penalties, as well as any potential reputational damage. Ultimately, the VCDPA is an important step forward in protecting the privacy of Virginia’s consumers and ensuring that Virginia businesses act responsibly with personal data.
Sensitive Content Communications and the VCDPA
Sensitive content communications are a vital part of ensuring compliance to regulations such as the Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA). To effectively protect personally identifiable information (PII) of Virginia residents, private sector businesses must have a system in place to track, control, and secure digital communications of PII. In the past, companies have relied on multiple tools and approaches to manage the different communications channels, such as email, file sharing, and APIs, leading to a fragmentation of metadata that makes it hard to maintain a centralized and automated system.
Kiteworks’ unified Private Content Network allows organizations to consolidate their sensitive communications involving PII. With Kiteworks, organizations track, control, and secure sensitive data shared and sent in and out of their organizations—all helping to ensure VCDPA compliance. Schedule a custom demo today to learn about the Kiteworks Private Content Network.



